Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-27 Origin: Site
Picture your data center. If power goes out, operations halt immediately. Redundancy & generators play a crucial role in keeping everything running smoothly. Redundancy provides an extra layer of protection against power loss, while generators supply backup power instantly. Ensuring continuous operation is essential, and redundancy & generators help minimize downtime and reduce your worries.
Benefit | How it Helps You |
|---|---|
Redundancy | Prevents power interruptions |
Generators | Provide immediate backup power |
Redundancy is having extra power parts ready. These parts help keep things working if something fails. This lowers downtime and keeps important equipment safe.
Generators give backup power when the main power goes out. They work with redundancy setups to make sure electricity stays on and works well.
Regular testing and professional care of backup generators and power systems keep things safe. This helps stop surprise power loss and keeps everything running.

Redundancy means having extra parts ready if something breaks. In electrical power systems, redundancy gives you backup circuits or devices. These can take over and keep things working. You see this in places like data centers and hospitals. Losing power there can cause big problems. Independence is important. Redundant parts should not share the same risks. They should not be too close or use the same control system. This setup helps avoid single points of failure. For example, double busbar systems and separate switchboards far apart help with this. They make the system more reliable. Redundancy tries to balance reliability with the extra work of adding more parts. It keeps your operations safe during problems or repairs.
Tip: Redundancy in power systems protects your equipment and data. It gives electricity another way to reach your devices. This keeps your business running even if something fails.
Redundancy Type | Description |
|---|---|
N | No redundancy. |
N+1 | One uninterruptible power supply and a backup. If one fails, the backup works. |
2N | Two uninterruptible power supplies. Each can give full power. One backs up the other. |
2N+1 | Uses both 2N and N+1 for extra safety. |
DN | Redundant rack power distribution units, but no UPS backup. |
DN+1 | Distribution redundancy plus N+1 UPS backup. |
Active redundant power supplies share the work. If one fails, the others keep going. Passive redundant power supplies have a main unit and a backup. The backup turns on only if the main fails. You see these types in data center redundancy setups.
Generators are the main backup power source. When the main power goes out, generators start by themselves. They give electricity to important systems. You need them in hospitals, data centers, and other places where power loss is not okay. Generators use fuel to make mechanical energy. Then they turn it into electrical energy. The fuel system keeps the generator running. Cooling and exhaust systems handle heat and fumes. The control panel starts and stops the generator during outages.
How generators work in backup power systems:
The engine uses fuel to make mechanical energy.
The alternator changes mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The fuel system keeps the generator running.
Cooling and exhaust systems handle heat and fumes.
The control panel manages starts and stops.
Generators give power to heating, cooling, refrigeration, and lighting. Standby generators start on their own during outages. They keep your home or business running without stopping. Most connect to your electrical system and use natural gas or propane. In data center redundancy, backup generators work with uninterruptible power supplies. This gives a smooth switch from grid power to backup power.
Note: Backup generators and emergency power supplies are very important for critical infrastructure. They give power during outages and protect sensitive equipment.
Redundancy & generators work together to lower downtime and protect your work. Without redundancy, you could lose power and face big problems. In important places like hospitals and data centers, one failure can stop everything. You might lose data, stop working, and hurt your reputation. The U.S. Department of Energy says equipment failures can cost millions each year. Redundancy in power systems keeps your IT equipment working and stops data loss.
Redundant power designs make things safer and more reliable. They lower the chance of outages and protect sensitive equipment. You avoid single points of failure, so one problem does not stop everything. Redundancy gives backup parts and systems that take over during failures. Setups like N+1 and 2N make sure you have power redundancy and more uptime. Data center redundancy helps you get almost perfect uptime and less downtime. Hospitals use many layers of power redundancy to keep life-support equipment working. Banks use redundancy & generators to keep trading going all the time.
Callout: Redundancy is like an insurance policy. It gives you more uptime, makes things reliable, and keeps important systems working during emergencies.
Redundancy & generators help you worry less. You know your work will go on even if something fails. Regular checks and tests of backup generators and uninterruptible power supplies keep your systems strong. You can focus on your business, knowing your power supply is safe.
Strong power redundancy keeps your data center safe. It helps systems keep working when power goes out. There are different types of power redundancy setups. Each type gives a different level of protection and uptime. The most common types are N, N+1, N+2, 2N, and 2N+1. These are used in data center redundancy plans.
Redundancy Type | Description | Fault Tolerance | Typical Use / Tier |
|---|---|---|---|
N | Minimum capacity, no backup. Any failure causes downtime. | None | Tier 1 |
N+1 | One backup for every N components. One failure tolerated. | One failure | Tier 2 or Tier 3 |
N+2 | Two backups for every N components. Two failures tolerated. | Two failures | High availability |
2N | Full duplication of all components. One set can fail. | Full | Tier 4 |
2N+1 | 2N plus one extra backup. Highest reliability. | Highest | Tier 4 |
As you move up, fault tolerance gets better. Higher levels mean more uptime and less risk. You pay more for higher redundancy, but you get stronger protection.
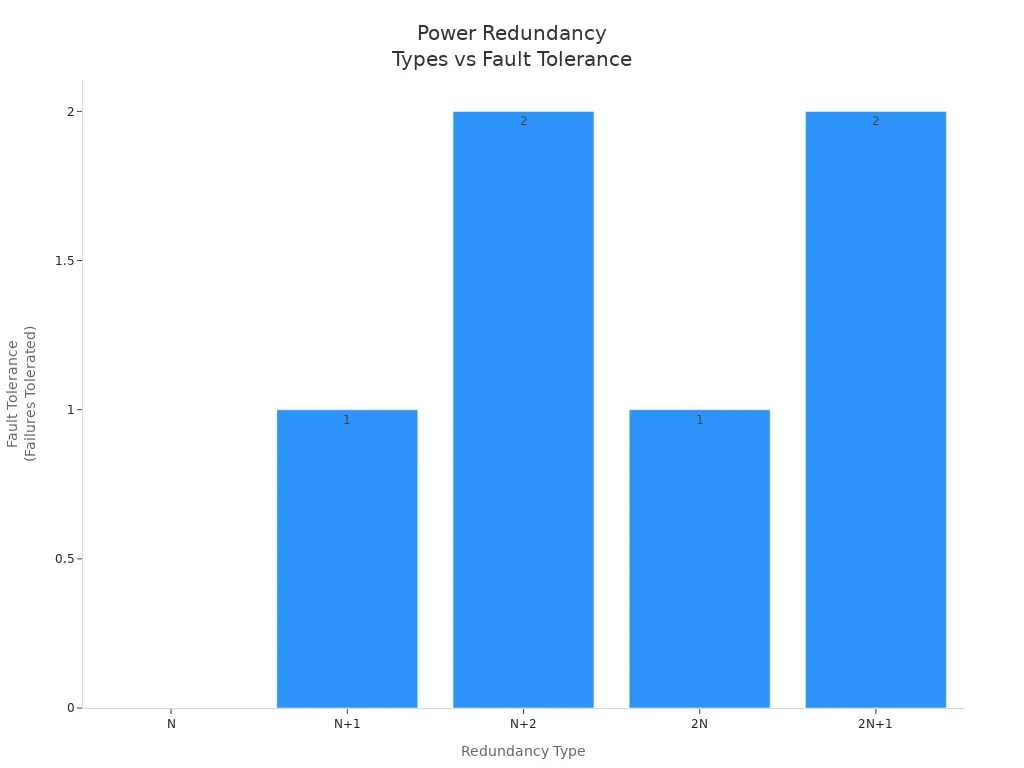
Power redundancy models are N, N+1, 2N, and 2N+1.
Data center redundancy matches your needs, budget, and risk.
Tier 1 uses N. Tier 2 has some redundancy. Tier 3 uses N+1. Tier 4 uses 2N+1.
More redundancy means more uptime, but costs more.
Power redundancy uses two utility feeds, UPS systems, and backup generators.
Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS) switch power sources fast during outages.
New tech includes renewable energy, AI monitoring, and battery storage.
Tip: Pick the right data center redundancy for your business. More redundancy keeps your data safe and systems working.
N+1 and 2N are common in data center redundancy. These setups give strong protection from outages. N+1 means one extra backup for each main part. If one fails, the backup takes over. 2N means two full sets of everything. One set can fail, and the other keeps working. You get full fault tolerance.
Configuration | Description | Redundancy Level | Applicable Tier | Impact on Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
N+1 | One backup for each main part. Keeps running if one fails. | Single backup | Tier 2 or Tier 3 | Improves uptime, reduces downtime, allows maintenance without stopping |
2N | Two full sets. Each can run everything alone. | Full duplication | Tier 4 | Highest fault tolerance, protects against failures, keeps power on during outages |
Data Center Tier | Redundancy Configuration | 2024 Revenue Share | CAGR | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Tier III | N+1 | 57% | N/A | Concurrent maintainability, distributed UPS, dual power strips |
Tier IV | 2N | N/A | 8.7% | Fault tolerant, 2N electrical paths, redundant utility feeds, 72+ hours fuel reserves |
Tier III & IV Combined | N+1 and 2N | 70% | 6.8% | Leading market share, high uptime, fault tolerance |
Tier III and Tier IV data centers use N+1 and 2N redundancy. These types cover most of the market. You get high uptime and strong protection from outages. Tier III uses N+1 for generators and transformers. It uses 2N for UPS and power distribution. Tier IV uses 2N everywhere. You get the best reliability and uptime.
Tier Level | Redundancy Type | Uptime Guarantee | Downtime per Year | Reliability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Tier III | N+1 | 99.982% | ≤ 1.6 hours | Allows maintenance, improves availability |
Tier IV | 2N or 2N+1 | 99.995% | ≤ 26.3 minutes | Fault tolerant, no single points of failure, highest reliability |
Note: Choose N+1 or 2N based on your risk and budget. More redundancy means less downtime and better protection.
Backup generators are needed for data center redundancy. You can group generators in parallel to boost capacity and redundancy. Parallel generators share the work. If one fails, others keep running. You get power even during maintenance or outages.
Parallel generators give flexibility. You can take one offline for service and still have power.
They improve reliability. If one fails, others pick up the load.
You can use smaller units together. It makes maintenance easier.
You can add more generators as your power needs grow.
Parallel operation handles changing loads better than one big generator.
Switchgear helps manage parallel generators. It balances loads and keeps voltage steady. Digital controllers help monitor and control each generator. You can service one unit while others run. You avoid downtime and keep your data center safe.
Running multiple generators in parallel gives redundancy. You keep power during maintenance.
You can wait longer between service periods. You save fuel by running only what you need.
Parallel generators adjust to demand. They turn on or off as needed.
You avoid shutdowns during servicing. You keep operations going.
Cause of Power Outage | Description | How Redundancy Mitigates Risk |
|---|---|---|
Power Grid Issues | Problems in the outside grid from storms or disasters. | Backup generators and UPS keep power on. Redundancy gives you layers of backup. |
Overvoltage Spikes | Surges from lightning or bad wiring. | Protector devices and redundant power supplies stop damage and shutdowns. |
Cooling and Airflow Problems | Bad cooling overheats servers. | Redundant cooling and monitoring keep temperature safe. |
On-Site Power Distribution | Failures in PDUs cause outages. | Redundant PDUs, load balancing, and maintenance keep power steady. |
Circuit Overloading | Too much power trips breakers. | Load balancing and policies spread power evenly. |
You face risks from outages, hardware problems, and human mistakes. Power redundancy and backup generators protect you. You get layered UPS, failover systems, and regular testing. Load balancing stops overloads. Real-time monitoring helps you spot problems fast.
Alert: Redundancy protects your data. It keeps your data center running during outages, cyberattacks, and disasters.
Redundant power sources and backup generators help fight cyberattacks. You get more power feeds and backup systems. If hackers attack the grid, your backup generators keep power on. You avoid downtime, data loss, and damage to your reputation. You keep your business safe.
You need data center redundancy to keep systems running. You use power redundancy, backup generators, and extra power lines. You get more uptime and less risk from outages. You protect your data and your business.
When picking generators for redundancy, match the power output to what you need. Figure out how much power your building uses. This helps you avoid getting a generator that is too big or too small. Pick a generator that can handle all your equipment or just the most important ones. Add a little extra, about 20-25%, for future needs. Think about what kind of fuel you want to use and how big the tank should be. Make sure you follow local rules. Diesel and gas generators both work well for backup. LIYU Group has gas generators and containerized gas generator solutions. These products help you get redundancy and steady power. Look for automatic transfer switches so power changes over smoothly. Use enclosures to protect generators from bad weather. Remote monitoring systems send alerts right away. Pick trusted brands and good installers. Always check that everything meets safety and environmental rules.
Tip: The right backup systems keep your business safe from losing money.
You need a good plan to install generators. Hire trained people to do the job. Put generators where air can move around them. Do not put them near air intakes. If you use more than one generator, use load sharing. This keeps power balanced and stops overloads. Automatic transfer switches help you change power sources fast. Plan for enough fuel to keep generators running if the power is out for a long time. Use docking stations for temporary power during repairs. Always use the best ways to set up power redundancy.
Key Implementation Steps | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
Professional installation | Keeps things safe and follows rules |
Load sharing setup | Makes sure power stays on |
Fuel management | Lets backup run longer |
Remote monitoring | Finds problems early |
Regular care keeps generators ready to use. Test them every month with a real load. Check the oil, filters, and battery to make sure they work. Look at the fuel system so it does not fail. Plan load bank tests to check the power output. Use certified technicians for checks. Follow the maker's checklist. Get a maintenance agreement if you do not have your own team. Keep records of all the work done. These steps make sure your backup power works and your redundancy plan is strong.
Alert: If you skip maintenance, your generator might not work when you need it.
Redundancy and generators help keep power on. Using N+1 or 2N setups means less downtime. Doing regular maintenance keeps your system working well.
Test your backup many times
Ask experts to help you plan
Check out LIYU Group's gas generator solutions for more steady power
Reliable power begins when you pick the right setup and take care of it.
N+1 means you have one more generator than needed. If one stops working, the extra one turns on. This way, you still have power and do not lose time.
Test backup generators once a month with real power use. This makes sure they work well if there is an emergency.
You can use different generator types, but they must have the same voltage and frequency. The table below helps you see the choices:
Generator Type | Fuel | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
Diesel | Diesel | Data centers |
Gas | Natural gas | Hospitals |
Portable | Gasoline | Small offices |
Tip: Always make sure different generators work together before you connect them.
Liyu Group Participates in Madagascar Government Delegation Forum
Liyu Group Invited to the China-Zambia Green Power Cooperation Forum
What Types of Facilities Benefit From Used Commercial Generators?
How Fuel Polishing Improves The Efficiency of Diesel Generators?
How Tariffs Could Potentially Impact The Generator Industry?