Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-01 Origin: Site
A 2-stroke engine finishes its power cycle in two strokes. A 4-stroke engine needs four strokes to do this. So, a 2-stroke engine makes power every time the crankshaft turns. This makes it lighter and easier to build. A 4-stroke engine works better and makes less pollution. Many motorcycles and small machines still use 2-stroke engines. This is common in Asia Pacific. But 4-stroke engines are becoming more popular. This is because there are more rules about pollution now.
LIYU Group has advanced gas generators and containerized gas generator sets. These are great for people who want engines they can trust.
2-stroke engines make power with every crankshaft turn. They are lighter and stronger for their size. But they use more fuel and pollute more.
4-stroke engines need four strokes to finish their power cycle. They run smoother and save more fuel. They pollute less and last longer.
2-stroke engines are simple and easy to fix. They work well for small tools and dirt bikes. They are good for light vehicles that need quick power and low weight.
4-stroke engines have more parts and need more care. They are best for cars, generators, and big machines. These engines give steady, clean, and strong power.
Pick a 2-stroke engine for fast, light, and cheap power. Pick a 4-stroke engine for saving fuel, quiet running, and long-lasting use.
The power cycle shows how engines make energy from fuel. A 2-stroke engine finishes its cycle in one crankshaft turn. It does intake, compression, combustion, expansion, and exhaust in two strokes. A 4-stroke engine needs two crankshaft turns to finish its cycle. It splits the process into four strokes: intake, compression, power, and exhaust.
The 2-stroke engine does all cycle steps in one turn. It makes power every time the crankshaft spins.
The 4-stroke engine needs two turns for one cycle. It makes power every other turn.
Because of this, the 2-stroke engine gives power more often. The 4-stroke engine runs smoother and uses energy better.
The table below compares both engines:
Aspect | 2-Stroke Engine | 4-Stroke Engine |
|---|---|---|
Crankshaft Revolutions/Cycle | 1 (360°) | 2 (720°) |
Power Stroke Frequency | Every turn | Every other turn |
Cycle Events | Combined | Separated |
Power-to-Weight Ratio | Higher | Lower |
Smoothness | Less smooth | Smoother |
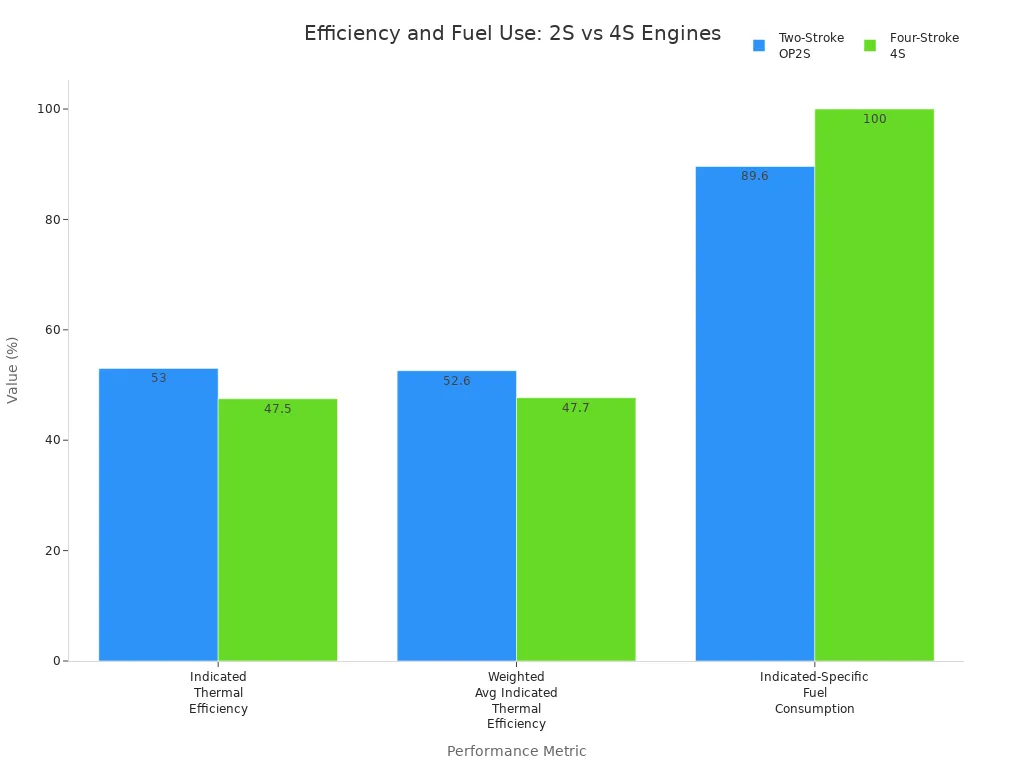
The chart above shows some 2-stroke engines can use fuel better. They also can be more efficient than regular 4-stroke engines. The 2-stroke engine fires twice as often. This gives it more power for its size. It works well when you need high power and low weight.
Mechanical design makes these engines different. The 2-stroke engine uses ports to move gases. It does not need valves or camshafts. This makes it lighter and easier to fix. The 4-stroke engine uses valves, camshafts, gears, and chains. It has more parts and is heavier.
The 2-stroke engine is simple and has fewer parts. It uses three ports: inlet, exhaust, and transfer.
The 4-stroke engine is more complex. It uses valves, camshafts, and extra gears.
The 2-stroke engine is lighter and smaller. It needs a lighter flywheel.
The 4-stroke engine is heavier. It needs a heavier flywheel for smooth power.
The 2-stroke engine is easier to fix because it is simple. The 4-stroke engine takes more time and skill to repair.
Aspect | 2-Stroke Engine | 4-Stroke Engine |
|---|---|---|
Cycle Completion | 1 crankshaft turn | 2 crankshaft turns |
Components | Ports (no valves) | Valves, camshafts, gears, chains |
Moving Parts | Fewer | More |
Weight & Size | Lighter, smaller | Heavier, bigger |
Maintenance | Easier | More complex |
Mechanical Efficiency | Higher | Lower |
Note: The simple 2-stroke engine is good for small tools and vehicles. The 4-stroke engine is more complex. It works better for cars and big machines because it runs smoother.
Fuel and oil systems are very different in these engines. The 2-stroke engine mixes oil with fuel. This mix keeps the engine parts slippery as it burns. The oil burns up and does not come back. The 4-stroke engine has a separate oil tank. Oil moves through the engine, keeps parts slippery, and goes back to the tank to be used again.
Aspect | 2-Stroke Engine | 4-Stroke Engine |
|---|---|---|
Lubrication System | Oil mixed with fuel; burns up | Separate oil tank; oil moves in a loop |
Lubrication Effectiveness | Not as good; oil burns away | Better; oil keeps working and cools parts |
Engine Longevity | Shorter life from more wear and dirt | Longer life from less wear and cleaner oil |
Emissions | More pollution because oil burns | Less pollution; oil does not burn |
Maintenance | Easier but needed more often | Harder but needed less often |
Oil Characteristics | Lighter, burns with fuel | Thicker, has cleaners and protects parts |
The 2-stroke engine's oil and fuel mix causes more pollution. It also needs fixing more often. Burning oil makes the engine wear out faster. The 4-stroke engine keeps oil inside. This helps the engine last longer and makes less pollution.
A study showed some 2-stroke engines use less fuel, up to 8.3% better than others. But, oil use in 2-stroke engines goes up when they run fast. It can be 10% to 27% higher at high speeds. The 4-stroke engine keeps oil use low and steady because it has a separate oil system.
Tip: If you want an engine that lasts longer and is cleaner, the 4-stroke engine is better for fuel and oil use.
If you need strong power for work or home, LIYU Group has advanced gas generators and containerized sets. These use trusted engine designs for good performance and efficiency.
A 2-stroke engine finishes its power cycle in two piston moves. This design lets it make power every time the crankshaft turns. The steps are simple:
The piston goes down from the top. This lets a new air-fuel mix enter the crankcase.
When the piston moves up, it squeezes the mix inside the cylinder. The spark plug lights the mix, and the piston goes down again.
As the piston goes up, the inlet port opens. This pulls in a new mix to the crankcase.
On the next down move, exhaust gases leave the cylinder. The new mix enters, and the cycle ends in one crankshaft turn.
This cycle happens fast. That makes the 2-stroke engine good for small machines and vehicles.
The 2-stroke engine gives quick power because it fires every turn. This means it has a high power-to-weight ratio and fast speed. Many small vehicles and tools use this engine for strong performance. The table below shows power ranges for different 2-stroke engine types:
Manufacturer / Engine Type | Engine Displacement (cc) | Power Output Range (kW) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
RCV Engines (methanol) | 9.5 - 21.3 | 0.64 - 1.5 | Smallest engines around 0.64 kW |
O.S. Engines (methanol) | ~90 - 160 | 2.3 - 3.6 | Glow fuel engines, high rpm |
Modellmotoren (gasoline) | 53 - 212 | 1.9 - 5.7 | Petrol/oil mix, multi-cylinder up to 5.7 kW |
Evolution Engines (gasoline) | N/A | 2.8 - 8.1 | Gasoline/oil mix, up to 8 kW |
Desert Air Engines (gasoline) | 100 - 150 | 7.3 - 12.3 | Larger engines, up to 12.3 kW |
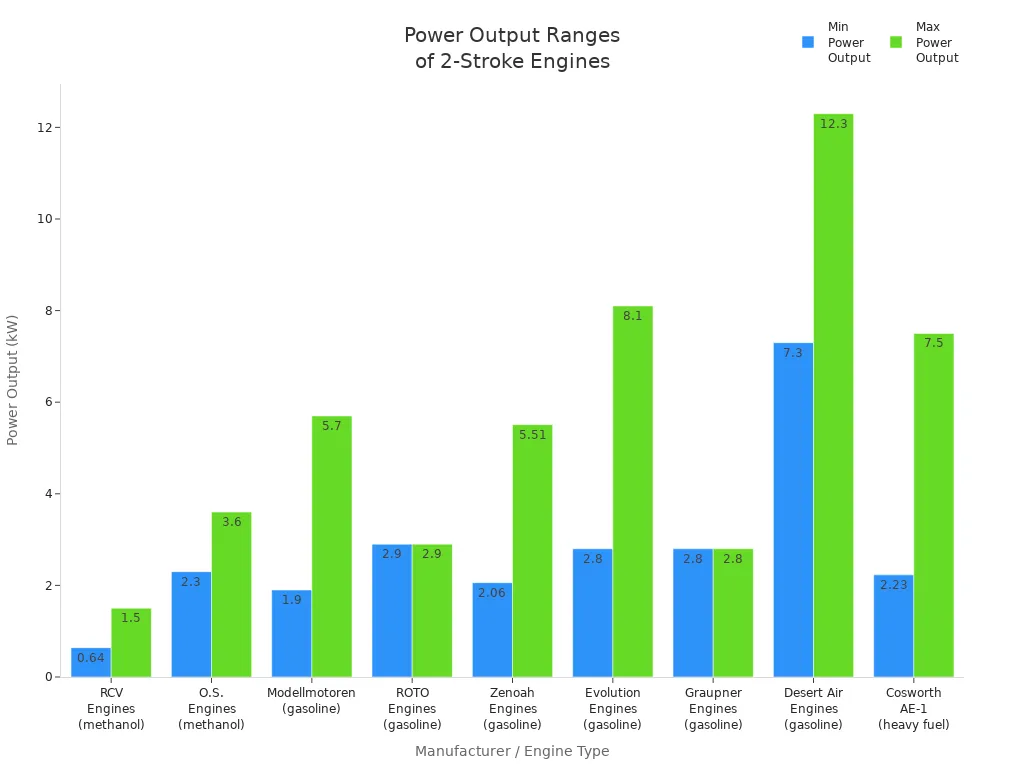
A 2-stroke engine speeds up faster than a 4-stroke engine. It is lighter and fires more often. It works well in racing bikes and chainsaws. But it makes less torque at low speeds. It is best for jobs where speed and light weight are important.
Taking care of a 2-stroke engine needs regular work. The fuel-oil mix burns oil, so you must change oil often to stop wear. Owners change filters often to keep the engine clean. They adjust injectors and timing to keep it running well. Old gaskets and seals need to be replaced to stop leaks. After many hours, parts like pistons and liners may need fixing. Many extra parts make repairs easier and cheaper. Good planning for care keeps the engine working well and lasting longer.
Tip: Regular care helps a 2-stroke engine last longer. It stops breakdowns and keeps machines working well.
A 4-stroke engine finishes its power cycle in four steps. Each step happens when the piston moves up or down. The crankshaft must turn two times for one cycle. The four strokes are:
Intake: The piston goes down. The intake valve opens. Air and fuel go in.
Compression: The piston goes up. The valves close. The mix gets squeezed.
Combustion (Power): The spark plug fires. The piston goes down. Power is made.
Exhaust: The piston goes up again. The exhaust valve opens. Burned gases leave.
This cycle keeps repeating. The spark plug fires once every two turns. The 4-stroke engine uses valves and a separate oil system. It does not need oil mixed with fuel. This design helps the engine stay cleaner and last longer.
The 4-stroke engine makes power every other crankshaft turn. It does not give as much power as a 2-stroke engine. But it uses fuel better. The engine burns fuel more fully. It also controls air and exhaust better. This means less pollution and better gas mileage.
A study showed the 4-stroke engine has a higher compression ratio. It also controls burning better. These things help it use less fuel and make more heat energy.
Tip: The 4-stroke engine helps save gas and makes less pollution. It is good for people who want to spend less and help the planet.
The 4-stroke engine lasts longer than a 2-stroke engine. It has a separate oil system. This keeps parts clean and stops them from wearing out fast. Many 4-stroke outboard engines run for 3,500 to 5,500 hours if cared for. Some people say their engines last over 4,500 hours before big repairs. Car engines with this design often go over 100,000 miles.
4-stroke engines do not need fixing as often.
They can handle hard work and heavy loads.
They wear out slower because oil does not burn away.
A 4-stroke engine is best for people who want a strong, long-lasting machine. It is the best choice for cars, generators, and big tools.
Note: LIYU Group has advanced gas generators and containerized sets. These use trusted 4-stroke engine designs for strong power and long life. People who need steady power can find great choices with LIYU Group.
The 2-stroke engine is known for being simple and strong. Many people pick it for small tools and machines. Here are the main good things about a 2-stroke engine:
It makes power every time the crankshaft turns. This means it has a lot of power for its weight.
It has fewer moving parts. It is smaller and lighter than other engines.
Its simple design makes it cheaper to make and easier to fix.
It uses ports instead of valves. This lowers the chance of something breaking inside.
Being light is good for jobs where weight matters.
It gives steady motion because it fires every turn.
Tip: These good things make the 2-stroke engine great for chainsaws, dirt bikes, and small boat motors.
But there are also some bad things about a 2-stroke engine:
It burns oil mixed with fuel. This makes more smoke and pollution.
Some fresh air and fuel escape through the exhaust port. This wastes fuel and adds to pollution.
It does not use fuel well. It needs more fuel to do the same work.
It wears out faster because the oil burns away. It needs fixing more often.
It can make big clouds of oily smoke, especially when old.
Note: These bad things make the 2-stroke engine less good for the environment and not as good for long use.
The 4-stroke engine is common in cars, generators, and big machines. It has many good points:
It burns fuel better. This helps it use less gas and go farther.
It makes less pollution. It meets tough EPA rules and helps keep the air clean.
It is quieter. It does not make as much noise and bothers animals less.
It has a separate oil system. This keeps parts clean and helps the engine last longer.
It does not need repairs as often. It is stronger and lasts longer.
Tip: These good things make the 4-stroke engine a smart choice for people who want a cleaner, quieter, and longer-lasting engine.
Still, there are some bad things about a 4-stroke engine:
It has more parts like valves and camshafts. This makes it heavier and harder to understand.
It costs more to make and fix. Repairs can be harder and cost more money.
It makes power less often. It can feel slower and not as quick as a 2-stroke engine.
The extra weight can make it not as good for small, easy-to-carry machines.
Aspect | 2-Stroke Engine | 4-Stroke Engine |
|---|---|---|
Power Delivery | Every crankshaft turn | Every other crankshaft turn |
Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
Complexity | Simpler | More complex |
Maintenance | Easier, more frequent | Harder, less frequent |
Fuel Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
Emissions | Higher | Lower |
Longevity | Shorter | Longer |
Note: The bad things about a 4-stroke engine are that it is heavier and more complex. This can make repairs cost more and power feel slower.
A 2-stroke engine is used in many places. It is good when light weight and fast power are needed. People see it in small tools and vehicles. Chainsaws, leaf blowers, and string trimmers use this engine. These tools are easy to carry and start quickly. Dirt bikes and off-road motorcycles use it too. They speed up fast and are simple to fix.
In boats, the 2-stroke engine is important. Small boats, fishing vessels, and ferries use it a lot. It is trusted and saves fuel. It works well with heavy loads and can run for hours. The table below shows where it is used and why:
Equipment Type | Why Use 2-Stroke Engines? | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Chainsaws, trimmers | Light, easy to carry, quick response | Stihl MS 170, Husqvarna 128LD |
Off-road motorcycles | Fast acceleration, simple design | Yamaha YZ125, KTM 250 SX |
Small boats, ferries | Reliable, fuel-efficient, durable | Water taxis, fishing boats |
Note: A 2-stroke engine is best for jobs needing light weight, speed, and easy care.
A 4-stroke engine powers many big machines. It is found in cars, trucks, and street motorcycles. It also runs generators, tractors, and building equipment. These engines last long and use less fuel. They are good for long trips and hard work.
A 4-stroke engine helps hospitals, mining trucks, and farm tractors. It gives smooth power and meets tough pollution rules. The table below lists where it is used:
Sector | Common 4-Stroke Engine Applications |
|---|---|
Transportation | Cars, trucks, buses, street motorcycles |
Energy | Generators, backup power, microgrids |
Construction & Mining | Excavators, loaders, mining trucks |
Agriculture | Tractors, harvesters, irrigation pumps |
Big garden tools like lawn mowers and tillers use 4-stroke engines. They give steady power and need fewer repairs.
Tip: A 4-stroke engine is great for people who want clean air, save fuel, and have machines that last.
Picking the best engine depends on what matters most to you. Some people want engines that are fast and light. Others care about saving fuel or having a quiet engine. Some want an engine that lasts a long time. Each engine type has its own good points.
The table below shows how they compare:
Factor | 2-Stroke Engine | 4-Stroke Engine |
|---|---|---|
Efficiency | Uses more fuel, less efficient | More fuel-efficient |
Weight | Lighter, simple design | Heavier, more parts |
Durability | Wears faster, less durable | More reliable, lasts longer |
Power | Quick acceleration, high power-to-weight | Smoother, steady power |
Maintenance | Simple, more frequent | Complex, less frequent |
Environmental | More emissions, louder | Cleaner, quieter |
Price is important when picking an engine. Two-stroke engines cost less to buy and fix. They have fewer parts, so repairs are easier. Four-stroke engines cost more at first and to repair. You need to change oil and filters, which costs extra. Over five years, two-stroke engines are often cheaper to own. Four-stroke engines save money on fuel and last longer.
Tip: If you want a light and fast engine for short jobs, pick a two-stroke engine. If you want quiet, clean, and long-lasting power, pick a four-stroke engine.
Think about these questions before you choose:
Do you want quick power or steady power?
Is saving money more important than saving fuel?
Will you use the engine where noise or pollution matters?
Picking an engine depends on what you need most. Two-stroke engines make more power for their size. They are lighter than four-stroke engines. But they need fuel mixed with oil. They also make more pollution. Four-stroke engines are cleaner and last longer. They use fuel in a better way. The table below shows how they are different:
Feature | 2-Stroke | 4-Stroke |
|---|---|---|
Power | Higher per weight | Smoother, steady |
Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
Maintenance | Simpler, frequent | Complex, less often |
People should pick engines that fit their power and efficiency needs. They should also think about how long the engine will last. LIYU Group has gas generators and container sets. These give strong and steady performance. If you need, contact LIYU Group now!
A 2-stroke engine completes its power cycle in two moves of the piston. A 4-stroke engine needs four moves. This makes the 2-stroke engine lighter and more powerful for its size.
A 4-stroke engine usually lasts longer. It uses a separate oil system that keeps parts cleaner. This design helps reduce wear and extends engine life.
A 2-stroke engine burns oil mixed with fuel. This process creates more smoke and pollution. The oil does not get reused, so it burns away each time.
People often see 2-stroke engines in chainsaws, dirt bikes, and small boats. These engines work well in tools and vehicles that need to be light and fast.
People should think about what matters most. If they want more power and less weight, a 2-stroke engine works well. If they want cleaner air and longer life, a 4-stroke engine is better.