Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-16 Origin: Site
You want to make a generator quieter. Maybe you hear noise in your yard. Your business may have loud machines at work. Many people think all generators are loud. But new technology has changed this. New designs use sound-dampening features. Now, the noise can be as soft as a fridge. Attenuation is important for more than comfort. Noise pollution can bother neighbors and break rules. To avoid noise problems, use sound-proof generator rooms. Try smart placement and simple sound barriers. These steps help make a generator quieter. They also lower noise pollution and improve the sound around you. Attenuation is important for many reasons. You protect your health, follow rules, and enjoy peace. You do not need to be an expert to do this. Start with easy sound reduction tips and notice the change. Remember, attenuation and noise reduction always matter. This is true at home or at work. Generator Basics show that sound can be managed. You can make a generator quieter with the right steps. You can also lower noise pollution with good sound solutions.
Generator noise can bother people and hurt health. Lowering noise helps people feel better and work better.
Placing generators in the right spot is important. Put them far from buildings and in open areas to lower sound.
Use things like walls and fences to block and move noise away. Using more than one barrier works even better.
Materials like mass-loaded vinyl and soundproof blankets help lower noise a lot.
Keeping generators in good shape and using anti-vibration mounts can cut down extra noise even more.
When you start learning about generator basics, you see why noise is a problem. Generator noise can bother you at home or at work. It can make it hard to relax, sleep, or pay attention. In factories, noise can make people less productive and more stressed. Here are some ways generator noise can affect you:
Generator noise can interrupt daily life at home or work.
Loud noise can hurt how well you work, your mood, and make you feel anxious.
Being around loud noise for a long time can cause health problems like hearing loss and heart issues.
Many studies show that being around loud noise for a long time can cause more than just hearing problems. It can lead to mental health issues like anxiety and depression. It can also raise your risk for high blood pressure, mess with your hormones, cause problems during birth, make it hard to sleep, and increase your chance of heart disease.
You should know that noise pollution from generators can break local laws. This can make neighbors complain or get you fined. Generator basics show that controlling noise is not just for comfort. It is also important for your health and to follow the rules.
To understand generator basics, you need to know some key words. Here are a few you will see a lot:
Noise: Unwanted sound that bothers people or nature.
Sound: Vibrations that move through air and reach your ears.
Noise pollution: Bad or annoying noise, often from machines like generators.
Sound attenuation: Making sound less strong by using special materials or designs.
Soundproofing: Stopping sound from getting in or out of a place.
Sound attenuation and soundproofing are different. Sound attenuation makes sound weaker by soaking it up or bouncing it away. Soundproofing keeps sound from moving in or out of a room. When you learn about generator basics, you see both ways help control noise.
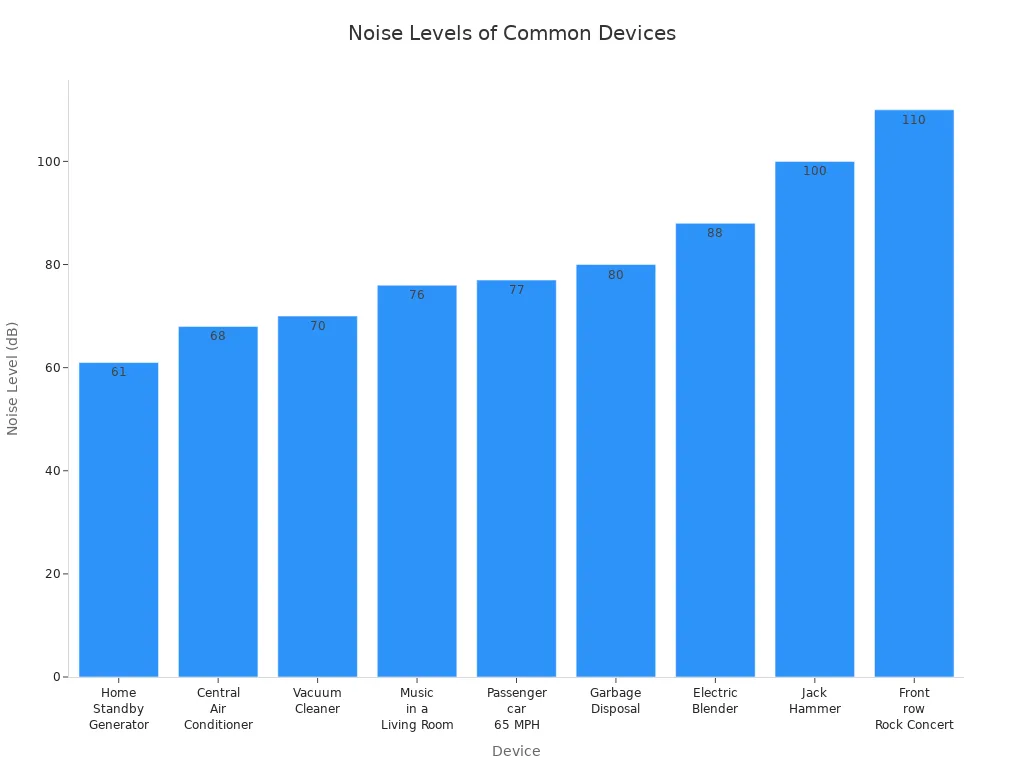
You might wonder how loud a generator is compared to other things. Here is a table to show you:
Device | Noise Level (dBA) |
|---|---|
Passenger car going 65 MPH @ 25 feet | 77 dBA |
Music in a Living Room | 76 dBA |
Vacuum Cleaner | 70 dBA |
Central Air Conditioner @ 20 feet | 68 dBA |
Garbage Disposal | 80 dB |
Electric Blender | 88 dB |
Jack Hammer | 100 dB |
Front row seats at a rock concert | 110 dB |
Home Standby Generator | ~61 dBA |
When you learn about generator basics, you also find out where the noise comes from in most generator designs:
Thermal noise
Shot noise
Vacuum diodes
Gas-discharge tubes
Zener diodes
Knowing these words and facts helps you see why noise control is important in generator basics. You can use what you learn to lower noise pollution and make your space quieter and safer.
If you want to stop generator noise, you need to know about sound attenuation methods. These ways help you make less noise and keep things quieter. You can use different types of attenuation to control noise pollution and make things more comfortable. Here are the main ways to lower noise.
Where you put your generator matters a lot for noise. You can make it quieter by picking a good spot. Put the generator in its own building or box. You can also move it far away from your building. This easy step makes things quieter for everyone.
Smart placement means putting the generator far from homes or work. If you put it on a roof or in a far spot, less noise reaches people. Do not put the generator in corners or close to walls. These places make sound bounce back and get louder. Open spaces let sound spread out and help air move, which keeps the generator cool.
Do not put the generator in small corners.
Use open spaces so sound can spread.
Add soundproofing materials to cut noise even more.
If you use these placement tips, you help stop noise and protect your community from noise pollution.
Sound deflectors help by sending sound away from people. You can use barriers like walls, screens, or fences. These block and bounce sound, making things quieter. The more barriers you use, the better it works.
You can put sound deflectors around homes or work areas. Many people use them in gardens or near buildings. They can look nice with plants and make outdoor spaces better. Sound deflectors work best when you use them with other sound attenuation methods.
Barriers like walls
Screens
Fences
Sound deflectors are important for stopping noise. They help you keep things peaceful.
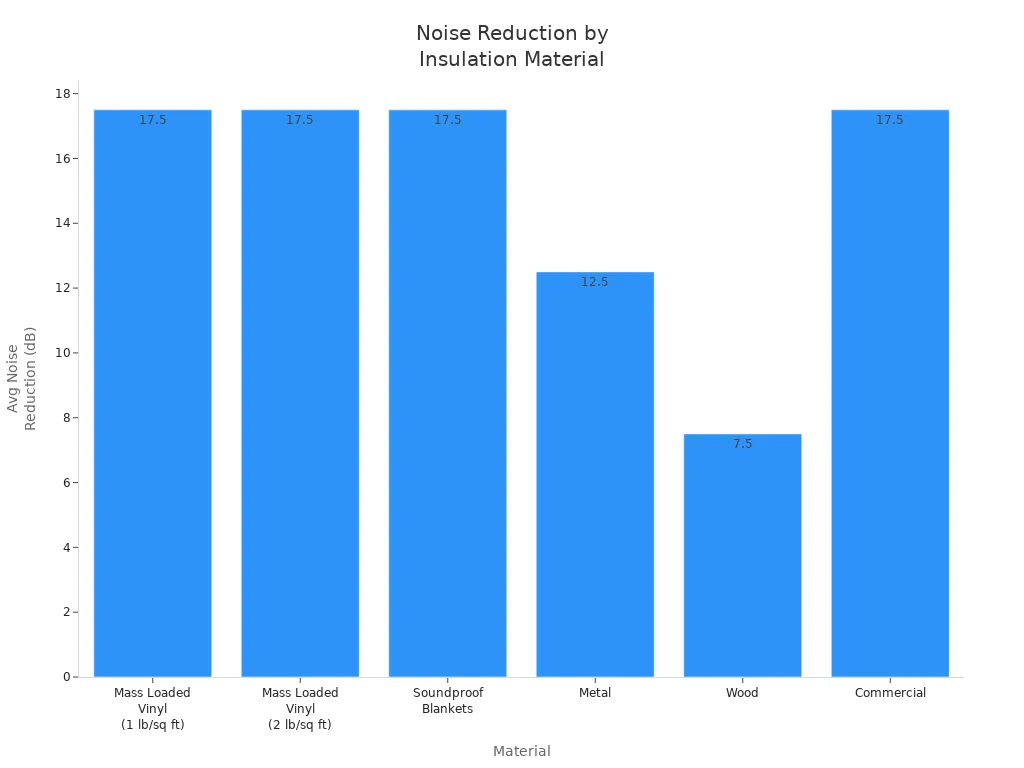
Acoustic insulation is another good way to stop noise. You can use special materials to soak up sound inside generator boxes. Mass loaded vinyl, soundproof blankets, metal, and wood are common choices. Each one blocks noise in a different way.
Material | Noise Reduction Capability (dB) |
|---|---|
Mass Loaded Vinyl (1 lb/sq ft) | 15-20 |
Mass Loaded Vinyl (2 lb/sq ft) | 15-20 |
Soundproof Blankets | 15-20 |
Metal | 10-15 |
Wood | 5-10 |
Commercial | 15-20 |
You can cover hard walls with sound-absorbing stuff. Soft things like ceiling panels, rugs, and wall covers help too. If you put sound absorption on two walls next to each other, you can cut echoes by 5-7 decibels. Try a checkerboard pattern for even better results.
The Liyu LY170 series gas generators use strong acoustic insulation and sound attenuation systems. These generators meet tough world rules for noise and emissions. They use good materials and smart design to control noise well.
Stopping vibration and unwanted sound is important for any generator. Anti-vibration mounts stop shaking from moving to the ground or buildings. You can use rubber mounts for small noise. Spring mounts are good for big generators. Advanced isolators are best for top-level needs.
Rubber mounts: Good for small generators.
Spring mounts: Best for big generators.
Advanced isolators: For the best vibration and unwanted sound reduction.
Put anti-vibration mounts under the generator. This soaks up shaking and keeps noise from spreading. You get quieter running and better sound control. Anti-vibration mounts are an easy way to help with vibration and unwanted sound.
Sound attenuators are special tools that help with noise. They use sound absorption and barriers to lower noise from generators. You can find sound attenuators as silencers, baffles, and boxes. These use soundproof materials and smart design to block and soak up sound.
When you pick sound attenuators, think about where the sound starts, how it travels, and who hears it. Good design and the right materials matter for noise control. Sound absorption composites turn sound into heat, which lowers noise. The Liyu LY170 series uses advanced sound attenuation to meet tough noise rules. These generators show how new designs can lower noise and control pollution.
Tip: Always think about cost and size when picking sound attenuation. More sound control can cost more and change airflow. Pick what works best for you.
You can use many types of attenuation to reach your noise goals. Signal processing for sound attenuation is another smart way. This uses technology to filter and cut unwanted noise. You can mix these ways for the best results.
Sound attenuation is both a science and an art. You can use placement, deflectors, insulation, mounts, and attenuators to control noise. Each way helps you lower noise pollution and make your space better. The right mix of materials and design helps you meet noise rules and enjoy quiet.
It is important to know the rules for noise attenuation before setting up a generator. These rules help keep people and nature safe from noise pollution. Many countries use worldwide standards to set sound limits. These limits help keep noise low and stop you from getting fined.
Here are the usual sound limits for generators:
In places with factories, the noise limit is 75 decibels (dB) during the day (6 a.m. to 10 p.m.) and 70 dB at night (10 p.m. to 6 a.m.).
These limits use the A-weighted scale, which matches how your ears hear sound.
You need to measure sound at the edge of your property or a certain distance from the generator. If you follow these rules, you help lower noise pollution and improve noise attenuation. You also protect your health and help people nearby feel comfortable. Good attenuation methods make it easier to stay within these sound limits.
Noise attenuation rules are different in each place. You should check your local laws before putting in a generator. Some places have strict sound rules, but others do not. This can change how you plan your noise attenuation steps.
Local rules about generator noise are very different in the United States and Europe. Europe has tougher rules that match international standards. U.S. rules have not changed much since the 1980s. The European Union has made laws that set noise limits for outdoor machines, including generators. These rules are not as strong in the U.S. This makes it hard for U.S. companies to compete in other countries.
Industries face many problems when trying to follow noise attenuation rules. You need to use the right sound attenuation methods to follow the law. Here are some common problems:
Challenge Type | Description |
|---|---|
Compliance with Local Ordinances | Industries must follow local noise rules that limit sound at different times and places. |
Technical Aspects of Noise Reduction | Using things like sound-attenuating enclosures and vibration isolation is needed. |
Importance of Regular Maintenance | Keeping generators in good shape helps them run quietly and not break noise rules. |
You can use noise attenuation tools like sound-attenuating enclosures, barriers, and vibration mounts. You can also pick a good spot for your generator to lower sound. These steps help you follow local rules and lower noise pollution.
Noise attenuation is not just about following rules. It helps protect your community from noise pollution. You make your space safer and more comfortable for everyone. When you use good attenuation methods, you show you care about the environment and other people.
Factories and big workplaces use noise attenuation a lot. Generators in these places can be very loud. The sound can travel far and bother many people. Noise attenuation helps keep the sound down. This makes the workplace safer and more comfortable for workers. The LY170 series generator is a good example. It works well in tough places and stays quiet.
Here are some ways noise control helps in factories:
You make the workplace quieter and more peaceful.
Workers can focus better and get more done.
Safety gets better and you follow noise rules.
You lower the chance of getting fined for loud noise.
You show you care about workers’ health.
You help your team stay strong and make your company look good.
Applications | Benefits of Attenuation |
|---|---|
Factories | Lower noise, safer work |
Construction | Less sound pollution |
Warehouses | Better sound control |
Power plants | Reliable generator operation |
Using noise attenuation in these places helps you follow the law. It also keeps everyone safe from too much noise.
Noise attenuation is also important at home. Generators in neighborhoods can be loud and bother families. Attenuation keeps the sound safe and your home quiet. The LY170 series generator is good for homes. It uses strong noise control systems.
Here are some ways noise control helps at home:
You follow sound rules from the State, Local, and OSHA.
You keep noise between 45 and 72 dB(A) at your property line.
You use quieter machines and noise control tricks.
You make sure your generator does not go over 75 dB.
Noise attenuation at home helps you avoid fights with neighbors. It also keeps your reputation good. You protect your health and enjoy a quieter place. Silent generators use less fuel and last longer. Sound enclosures can cut noise by up to 40 dB(A). You get new technology that lowers pollution and helps clean energy.
Tip: Using noise attenuation at work and home makes spaces healthier. You stop hearing loss and make things more comfortable for everyone.
Noise attenuation matters everywhere. You use it to control sound, stop noise pollution, and follow the rules. The LY170 series generator gives you strong noise control for many places.
You can make your generator quieter with simple steps. Try using plywood, mass-loaded vinyl, or sound blankets to block noise. The table below shows how each material works for sound attenuation and noise control:
Material | Sound Absorption | Durability | Easy to Move? |
|---|---|---|---|
Plywood | Medium | High | Yes |
Mass-loaded vinyl | High | Medium | Yes |
Sound blankets/tarps | High | Medium | Yes |
Acoustic foam panels | High (indoors) | Low | No |
Start by putting up a fence or planting shrubs to help soak up sound. You can also build a frame and add sound-absorbing panels for better results. Check your generator often and tighten any loose parts to keep it quiet. If you want more ideas, look for new soundproofing products or talk to experts about the best ways to lower noise. Take steps now to make your space quieter and enjoy less noise.
Sound attenuation makes sound weaker. Soundproofing keeps sound from getting in or out. Attenuation works by soaking up or bouncing sound away. Soundproofing blocks noise from moving through walls or barriers. Both ways help you control noise and feel more comfortable.
You can use a sound level meter to check noise. Put the meter in different places near your generator. Write down the noise levels in decibels. This helps you know if you follow local rules. Checking often helps you see changes and plan for better sound control.
Mass loaded vinyl, sound blankets, and acoustic foam work well. These materials soak up sound and lower noise. You can also use plywood or metal for extra help. Good materials help you reach your noise goals and make sound better.
Where you put your generator changes how sound moves. If you put it far from homes, you make less noise. Open spaces let sound spread out and help with attenuation. Do not put generators in corners or close to walls. Smart placement gives you better noise control.
Yes, you can use more than one method together. Try sound deflectors, acoustic insulation, and anti-vibration mounts. Each one helps with a different kind of noise. Using them together gives you stronger sound control. You get a quieter space and less noise pollution.
Liyu Group Participates in Madagascar Government Delegation Forum
Liyu Group Invited to the China-Zambia Green Power Cooperation Forum
What Types of Facilities Benefit From Used Commercial Generators?
How Fuel Polishing Improves The Efficiency of Diesel Generators?
How Tariffs Could Potentially Impact The Generator Industry?