You use a natural gas generator to make electricity. It burns natural gas inside an engine. This helps power homes, stores, and factories during blackouts or emergencies. In the United States, natural gas generators make about 39% of the country's electricity. People use these generators at home for backup. They keep lights and refrigerators working. They also help machines run in hospitals or factories. If you want steady power, think about LIYU Group's natural gas generator. You can also look at our containerized generator sets for your needs.
Natural gas generators give clean and steady electricity. They help during power outages and for daily use. They save money and make less pollution than diesel or gasoline models.
These generators burn natural gas in an engine. The engine moves pistons. The pistons spin an alternator. The alternator makes electricity for homes, businesses, and hospitals.
The main parts are the engine, alternator, fuel system, cooling system, and control panel. These parts work together to keep power steady and safe.
You should check oil, fuel lines, and batteries often. This helps your generator run well and last longer. It makes sure it works when you need it most.
Pick the right size generator for your needs. Use clean natural gas to make it work better. LIYU Group has good options for homes and businesses.
A natural gas generator gives you electricity when you need it. You can use it as backup during power outages. It also works as the main power source for homes, businesses, or hospitals. This generator uses natural gas instead of gasoline or diesel. The fuel comes through pipelines, so you do not need to store it. Many people pick natural gas-powered generators because they cost less to run. They start by themselves and make fewer harmful emissions.
Note: Natural gas generators burn cleaner than diesel or gasoline models. You help the environment when you choose this option.
You find natural gas generators in many sizes. Some only power a few lights and appliances. Others keep whole buildings running. The main job of a generator is to give electrical power when the main grid fails or you need extra energy.
Here is a quick look at how natural gas generators compare to other types:
Natural gas has lower energy density than diesel, so engines may be bigger for the same power.
You need a working gas pipeline; if a disaster breaks the line, the generator may stop.
Natural gas burns cleaner than diesel or propane, so it is better for the environment.
Propane stores in tanks, but natural gas comes through pipes, so you do not need to refill tanks.
Diesel generators give more power but cost more and pollute more.
You might wonder how a natural gas generator works. The process is easy to understand. The generator uses an internal combustion engine to turn natural gas into electricity. Here is a step-by-step overview:
The generator pulls in air from outside.
It squeezes the air inside the engine.
The fuel system sends natural gas into the engine.
A spark plug lights the air and gas mixture.
The explosion pushes a piston, which turns a crankshaft.
The crankshaft spins the alternator, making electricity.
The exhaust system removes gases from the engine.
You can see the main parts of a natural gas-powered generator in this list:
Engine: Turns fuel into movement.
Alternator: Changes movement into electricity.
Fuel system: Brings natural gas to the engine.
Voltage regulator: Keeps the electricity steady.
Cooling system: Stops the engine from getting too hot.
Exhaust system: Removes waste gases.
Lubrication system: Keeps engine parts moving smoothly.
Battery: Starts the engine.
Control panel: Lets you watch and control the generator.
Tip: Regular checks on the fuel system and cooling system help your generator last longer.
You can pick a generator based on your power needs. Here is a table that shows typical power output ranges:
Generator Type | Power Output Range (kW) | Examples / Notes |
|---|---|---|
Air-cooled Residential | 10 - 19.5 | Typical range for air-cooled whole house natural gas generators |
Air-cooled Residential (max) | Up to 26 | Generac Guardian Series (14 - 26 kW), Champion (12.5 - 22 kW), Briggs & Stratton (20 - 26 kW) |
Liquid-cooled Residential | 22 - 150 | Good for bigger homes, estates, or businesses |
Commercial Generators | 25 - 150 | Made for small to medium-sized businesses; includes Generac Protector Series (up to 60 kW), Cummins (22 - 60 kW) |
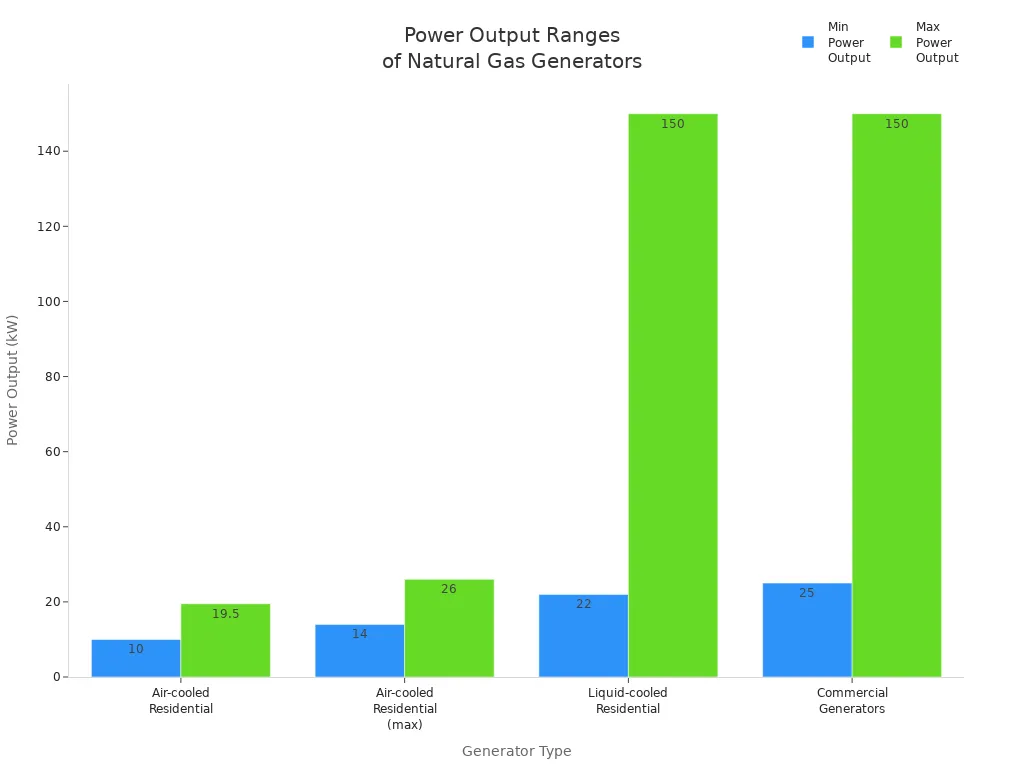
You use smaller natural gas-powered generators for homes. These usually give less than 25 kW, enough for lights, refrigerators, and heating or cooling. Bigger generators, up to 150 kW, power businesses, farms, or construction sites.
Callout: If you want a reliable and clean power source, think about LIYU Group's natural gas generator or our containerized gas generator sets.
The internal combustion engine is the main part of every generator. It uses natural gas to make mechanical energy. This engine runs on cheap natural gas, so you save money. It makes cleaner energy than petrol or diesel engines. You get less pollution and fewer emissions. The engine lasts longer because natural gas causes less damage. You spend less money fixing it. It works well for big power needs and keeps your generator working.
Changes natural gas into mechanical energy
Costs less to run
Makes cleaner energy with fewer emissions
Helps the engine last longer
Keeps the generator working well
Most generators have stationary reciprocating spark ignition engines. These engines use a spark plug to light the fuel-air mix. You find them in small and medium generator sets. Lean-burn gas reciprocating technology makes these engines work better. Digital controls and heat recovery systems help you get more from your generator.
The alternator turns the engine's mechanical energy into electrical energy. It uses electromagnetic induction to do this. The rotor spins inside a magnetic field. This spinning makes electricity in the stator windings. You get alternating current (AC) for your power. The alternator starts with a battery or a small generator. Then it becomes self-excited. Brushless alternators use an exciter for steady power.
Alternator Component | Function |
|---|---|
Rotor | Spins to make a magnetic field |
Stator | Has windings to make AC |
You need to check your alternator often. Cleaning and checking it stops overheating. This keeps your generator working well. Big generators use strong alternators for nonstop work.
Your generator needs a steady fuel supply to work. Natural gas comes through pipes, so you do not fill tanks. This system gives steady power to places like hospitals and factories. You get power that does not stop because the fuel keeps coming.
Leak-free design with regular checks
Pressure relief valves and regulators for safety
Shut off valves to close the system
Strong tanks tested for safety
Methane alarms and detectors
Explosion-proof equipment
Good airflow to lower risks
Safety features keep you and your generator safe. The fuel supply system follows strict rules to protect everything.
You use the starter and control panel to run your generator. The panel shows voltage, current, frequency, oil pressure, water temperature, engine speed, runtime, and fuel flow. Sensors watch for changes inside the generator. The microprocessor reads these signals and makes changes. If something is wrong, the control panel can turn off the generator to stop damage.
The transfer switch works with the control panel. It knows when the main power goes out. The switch tells the control panel to start the generator. The starter turns on, and when the generator is ready, the transfer switch moves your power to the generator. You get smooth power during blackouts.
Generators need cooling to stay safe. Small generators use air cooling. Fans blow air to keep them cool. Big generators use liquid cooling, like a car radiator. This makes them quieter and work better.
Some generators use hydrogen gas or liquid cooling for better heat control. These ways help your generator run longer and handle more work.
Exhaust systems lower noise and pollution. Special turbine exhaust systems make sound go from 150dB to 100dB. This protects your neighbors from loud noise. Carbon capture can trap up to 98.5% of CO2. There are also controls for methane and nitrogen oxide. These features help your generator meet clean air rules.
Your generator starts by pulling in natural gas and air. The intake system mixes them together for burning. Some generators use Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) to lower emissions and help burning. Diesel engines use high compression, but your generator uses spark plugs to start burning. This is like how a car engine works. The fuel comes through an Integrated Fuel Module, not regular injectors. Natural gas is already a gas, so it mixes with air easily. This lets the engine burn the fuel well and makes less pollution.
Some generators use Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI). In this method, the engine mixes natural gas and air before it goes into the cylinder. Sometimes, a little diesel is added to help start burning. The mixture gets squeezed until it gets hot enough to burn by itself. This way uses both spark and compression ignition. It gives you clean and efficient power.
Tip: Good fuel quality is important. Dirty fuel can cause bad burning and less power. Always use clean natural gas for the best results.
Other things can make ignition harder:
High places have thin air, so burning is harder.
Hot weather makes air thinner and can cause overheating.
Humid air has less oxygen, so burning may not work as well.
Doing regular maintenance, like changing oil and filters, helps your generator start and run well.
When the mixture burns, combustion happens inside the cylinder. This makes hot, high-pressure gases. These gases push the piston down hard. The piston moves back and forth from the burning fuel. This movement is what makes your generator work.
How the piston moves depends on the pressure and heat inside the cylinder. When the piston is at the top, the explosion pushes it down. The gas expands and the pressure drops. This changes the energy in natural gas into movement.
You can see how well this works by looking at these numbers:
Source / Study | Combustion Mode / System | Efficiency Type | Efficiency Value |
|---|---|---|---|
Sandia National Laboratory | Nearly constant volume combustion | Indicated thermal | Up to 56% |
Toyota Central R&D Labs Inc. | Premixed charged compression ignition | Thermal | 42% |
Free-piston engine generator model | General free-piston engine operation | Indicated thermal | 31.5% |
Most generators work between 31.5% and 56% efficient in this stage. This depends on how they are built and what technology they use.
Note: New engine designs and better burning methods can make generators work better and pollute less. Keeping your generator in good shape helps you get the most power from your fuel.
The piston's movement does not make electricity by itself. The generator uses a crankshaft to change this movement into spinning. The crankshaft connects to the rotor. As the piston moves, it turns the crankshaft. The crankshaft spins the rotor inside the generator.
The rotor acts like a magnet inside wire coils called the stator. When the rotor spins, it makes a magnetic field. This field makes electricity in the stator windings. This is how your generator changes movement into electricity.
Some generators use a belt to connect the crankshaft and rotor. The engine turns the crankshaft, the belt spins the rotor, and the rotor makes electricity. This is important for steady power.
Your generator's main job is to give steady power. You measure this power in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). To find out how much power you get, multiply voltage by current. For example, if your generator gives 100 volts and 3 amps, it makes 300 watts.
You can also measure energy over time in watt-hours (Wh) or kilowatt-hours (kWh). If your generator runs at 2000 kW for 720 hours, it makes 1,440,000 kWh. This helps you plan fuel use and check if your generator is enough.
To keep your power safe and steady, use the right size generator. Big generators waste fuel. Small ones can break if overloaded. Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS) help by switching between utility power and generator power. This way, you always have electricity during blackouts.
You can find a gas turbine in many power plants today. It makes mechanical energy by using heat from burning fuel. The main parts are a compressor, a combustion system, and a turbine. The compressor squeezes air and sends it to the combustion chamber. Fuel mixes with the air and burns at very high heat. This burning makes hot, high-pressure gas. The turbine takes energy from this gas and spins a shaft. This spinning shaft can power a generator or other machines.
Here is how a gas turbine works:
The compressor pushes air into the combustion chamber.
Fuel burns and makes hot gas.
The hot gas spins the turbine blades.
The shaft turns and powers a generator.
Gas turbines run quietly and have fewer moving parts than piston engines. They can use natural gas, diesel, or other fuels. You see them in power plants, airplanes, and ships. They start up fast and make lots of power in a small space.
Tip: Gas turbines are best when you need steady, strong power for a long time.
You might wonder how a gas turbine is different from a natural gas generator. Both make electricity, but they work in different ways. A natural gas generator uses a piston engine. It burns fuel and moves pistons up and down. The crankshaft turns and makes electricity. A gas turbine uses spinning motion all the time. It squeezes air, burns fuel, and spins turbine blades.
Here is a table to show the differences:
Feature | Gas Turbine | Natural Gas Generator (Piston Engine) |
|---|---|---|
Motion Type | Rotational (continuous) | Reciprocating (back and forth) |
Main Parts | Compressor, combustion, turbine | Engine, pistons, crankshaft, alternator |
Startup Time | Fast (minutes) | Fast |
Power Output | High for size | Scales well for small and large needs |
Efficiency | High at full power, lower at part load | Good at variable loads |
Maintenance | Fewer moving parts, lower cost | More moving parts, higher cost |
Fuel Types | Many (natural gas, diesel, biofuels) | Mostly natural gas |
Emissions | Low CO and hydrocarbons | Cleaner than diesel, but more than turbine |
Noise | High | Lower |
Gas turbines give you lots of power for their size. They run smoothly and do not need much fixing. You get steady power for big power plants. They work well in systems that use waste heat to make more electricity. You can use many kinds of fuel. Gas turbines have some downsides. They cost more to buy. They do not work as well at low power. They are louder and need special parts for high heat.
Natural gas generators with piston engines are better for homes and small businesses. They handle changing power needs and can be made smaller. You get good efficiency even when not using full power. They cost less and are quieter.
Note: If you need steady, strong power for a big project or plant, pick a gas turbine. For backup at home or a small business, a natural gas generator is better.
You want a generator that works well and saves money. Natural gas generators are cheaper to run than diesel ones. They use fuel from pipelines, so you do not need to store fuel. The type of generator changes how efficient it is. Diesel generators turn more fuel into power because diesel has more energy. Natural gas generators are less efficient, but they are still a good choice for most homes and businesses.
Generator Type | Efficiency (%) | Fuel Energy Density (Btu) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Diesel Generators | About 40 | 129 | Higher energy density, more fuel efficient |
Natural Gas Generators | Lower than diesel | 37 | Less efficient due to lower energy density |
Natural gas generators do not work as efficiently as diesel ones. Some big natural gas plants can reach over 60% efficiency. Most backup generators work at 35-42% efficiency. Even though they are less efficient, you save money on fuel and get steady power. You can use a standby generator at home or work and avoid high fuel costs.
Using a natural gas backup generator helps the environment. These generators make less pollution than diesel or coal. You get less carbon dioxide, less soot, and fewer bad gases. Natural gas burns cleaner, so the air around your home or business stays better.
Makes less carbon than diesel or coal
Less soot and smoke in the air
No fuel storage, so spills are less likely
Choosing a natural gas backup generator helps keep the world cleaner. Many cities like these generators for hospitals, schools, and homes.
You want your backup generator to work when you need it most. Doing regular checks keeps it ready to go. Run the generator every week to look for problems. Check for leaks, see if there is enough fuel, and make sure it is set to 'Auto.' Each month, check the oil, coolant, and battery. Clean the generator and look for loose wires or rust.
Generator Part | Typical Repair Cost Range |
|---|---|
Stator and Rotor | $250 to $1,500 |
Carburetor | $60 to $500 |
Engine | $50 to $2,000 |
Voltage Regulator | Around $80 |
Transfer Switch | $50 to $400 |
Yearly maintenance costs are between $1,000 and $2,000. This pays for oil changes, topping off coolant, checking the battery, changing spark plugs, and testing. You should also have a professional check your generator once a year. This keeps your standby generator ready for any power outage.
Tip: Following a regular maintenance plan helps your backup generator last longer and work better.
You can use a backup generator for homes, stores, hospitals, and factories. It gives you peace of mind during storms or blackouts. You do not have to worry about losing power for lights, fridges, or medical equipment.
Now you understand how a natural gas generator makes electricity from fuel. This kind of backup generator gives steady power when the lights go out. Using it saves you money and is better for the environment. You can count on a backup generator at home, work, or in a hospital. If you need power that does not stop, pick a backup generator. Look back at the main sections if you want more information. LIYU Group has both natural gas generators and containerized generator sets. You get clean, steady power for any need. Contact us to find the best choice for your business.
Most natural gas generators can run for days if gas keeps coming. Many home models work for at least 24 hours. Always read your generator's manual for safe running times.
You can use a natural gas generator for lights and refrigerators. It also powers air conditioners and medical equipment. Bigger generators can run whole homes or small businesses. Check your generator's wattage to know what it can handle.
Tip: Write down your most important devices before picking a generator.
No, never use a natural gas generator inside your house. It makes carbon monoxide, which is very dangerous. Always put your generator outside in a place with lots of fresh air.
Check your generator every week. Look at the oil, battery, and fuel lines. Have a professional do a full inspection once a year. Regular care keeps your generator ready for emergencies.
Task | How Often |
|---|---|
Check oil | Weekly |
Inspect battery | Monthly |
Full inspection | Yearly |
Liyu Group Participates in Madagascar Government Delegation Forum
Liyu Group Invited to the China-Zambia Green Power Cooperation Forum
What Types of Facilities Benefit From Used Commercial Generators?
How Fuel Polishing Improves The Efficiency of Diesel Generators?
How Tariffs Could Potentially Impact The Generator Industry?