Understanding generator spec sheets helps you choose wisely. When you read generator spec sheets, you learn how the generator works. You also see what the generator can do. You find important things like control panels, engine protection, and voltage regulation.
Control panels let you start, stop, and use emergency features.
Engine protection keeps the generator safe from low oil. It also protects from high temperature or sensor problems.
Voltage regulation gives steady power for your needs.
When you know what each spec means, you avoid mistakes. You pick a generator that fits your needs. You feel sure and make better choices.
Know the generator's duty cycle. Pick one that fits how you will use it. This helps you avoid damage and saves money.
Look at power ratings like kW and kVA. Match the voltage and phase to your equipment. This keeps power safe and steady.
Pick a fuel type that fits your budget and supply. Think about the environment too. This helps the generator work best.
Take care of your generator with regular maintenance. This helps it last longer and work well.
Compare spec sheets with tables or charts. Ask an expert for help. This helps you choose the best one for your needs.
When you check a generator spec sheet, you will see duty cycle. Duty cycle shows how long the generator can run. It also tells you what kind of work it can do. You should know the difference between standby, prime, and continuous duty cycles. Each one is made for a different job.
Here is a table to help you compare the three main generator duty cycles:
Feature | Standby Generators | Prime Generators | Continuous Generators |
|---|---|---|---|
Operation Duration | Short-term, emergency use | Extended, variable loads | Unlimited, steady load |
Load Variability | Not for variable loads | Handles variable loads | Constant, steady load |
Cooling System | Smaller, for short use | Larger, for longer use | Largest, for nonstop use |
Alternator Design | Less robust | Heavy-duty | Most robust |
Engine Speed | Higher speed (1800 rpm) | Lower speed (1200/900 rpm) | Lower speed (1200/900 rpm) |
Typical Applications | Backup during outages | Remote, off-grid, construction | Industrial, 24/7 power |
Standby generators are best for backup power. You use them when the main power goes out. They run for short times and only in emergencies.
Prime generators give power for longer times. You use them where there is no regular power. They can handle loads that change.
Continuous generators give power all the time. You use them when you need nonstop power. They work well for big factories or faraway places.
You need to match the duty cycle to your needs. Picking the wrong type can cause damage or make the generator fail. For example, using a standby generator every day will wear it out quickly. It does not have enough cooling or strong parts for long use. Prime and continuous generators have stronger engines and better cooling. They can run for many hours without stopping.
Tip: Always look at the duty cycle before buying a generator. This helps you avoid mistakes and keeps your power safe.
The right generator keeps your power steady and your equipment safe. You save money and avoid problems when you pick the correct duty cycle.
When you know generator specifications, you pick the right one. Generator spec sheets show many details. Each specification tells you something about power, output, setup, and how well it works. Let's look at the main specifications and see why they matter.
Power rating tells how much power a generator gives. You see two numbers: kW and kVA. kW is real power. It runs your machines. kVA is total power. It includes real and reactive power. The power factor connects kW and kVA. Most big generators use a power factor of 0.8. For example, a 125 kVA generator with 0.8 power factor gives 100 kW. You need to match generator size to your total load. Include surge loads and future needs. If the generator is too small, it gets too hot and breaks. If it is too big, it wastes fuel and costs more.
Tip: Always check both kW and kVA ratings. This helps you avoid weak systems and keeps your power steady.
Voltage and phase show if the generator fits your system. Single-phase generators work for homes and small shops. They give 120V or 240V. This is good for lights and small machines. Three-phase generators work for big places like factories and hospitals. They give 208V or 480V. This is best for heavy machines. Matching voltage and phase stops damage and keeps things safe.
Single-phase: One AC wave, good for light loads.
Three-phase: Three AC waves, good for big loads.
Note: Always match voltage and phase to your load and switch.
Fuel type changes how well the generator works. It also changes cost and pollution. You can pick diesel, natural gas, propane, biodiesel, or hydrogen.
Fuel Type | Efficiency | Cost | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
Diesel | High | Moderate | Moderate |
Natural Gas | Moderate | Low | Low to Moderate |
Propane | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
Biodiesel | Moderate to High | Moderate to High | Low |
Hydrogen | High | High | Very Low |
Diesel uses less fuel and lasts longer. It costs more and pollutes more. Natural gas burns cleaner and costs less. It needs a pipeline. Propane burns clean but uses more fuel. Biodiesel lowers pollution but costs more. Hydrogen makes no pollution but costs the most.
Tip: Pick a fuel type that fits your budget, supply, and rules.
Engine details show how strong and easy to fix your generator is. Check the fuel system, oil, cooling, and battery. Clean filters, good oil, and coolant stop problems. You need to check the engine often.
Look at fuel filters for dirt.
Change oil and grease moving parts.
Check coolant and radiator.
Test battery and clean ends.
Regular care keeps your generator working and saves money.
The model number helps you know the exact generator. It shows the series, size, and features. Use the model number to order parts, get help, and check if it fits.
Power factor shows how well the generator uses power. Most generators use a power factor of 0.8. Derating means lowering output because of high places or heat. At 1,000 feet, diesel generators lose 2-3% power. Natural gas generators lose about 5% per 1,000 feet. Hot weather also lowers power. You must figure out derating to make sure your generator is big enough.
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Derating for Gasoline/Diesel/LP Generators | 2-3% output reduction per 1000 feet elevation |
Derating for Natural Gas Generators | About 5% output reduction per 1000 feet elevation |
Continuous Use Load Recommendation | Best at 80% capacity |
Emergency Use | Can run at 100% capacity for short times |
Note: Always adjust for height and heat when picking your generator.
Physical size changes where you put your generator. Big generators need more space. You must follow local rules and get permits. You need a flat, strong base, usually concrete. Keep the area clear for air and repairs.
Pick a flat, strong spot near your panel.
Clear away trash and things in the way.
Put in a concrete pad bigger than the generator.
Bolt down the generator.
Get permits and plan inspections.
Clearance Aspect | Recommended Minimum Clearance |
|---|---|
Distance between generator and walls or obstructions | 5 feet |
Clearance to open generator doors for servicing | 3 feet 6 inches (42 inches) |
Clearance on all sides for commercial generators | 3 feet |
Clearance at backside for gas and electric inlets | 18 inches |
Clearance from combustible materials | 60 inches (5 feet) |
Working space for inspection and maintenance (NFPA 110-2022) | 36 inches |
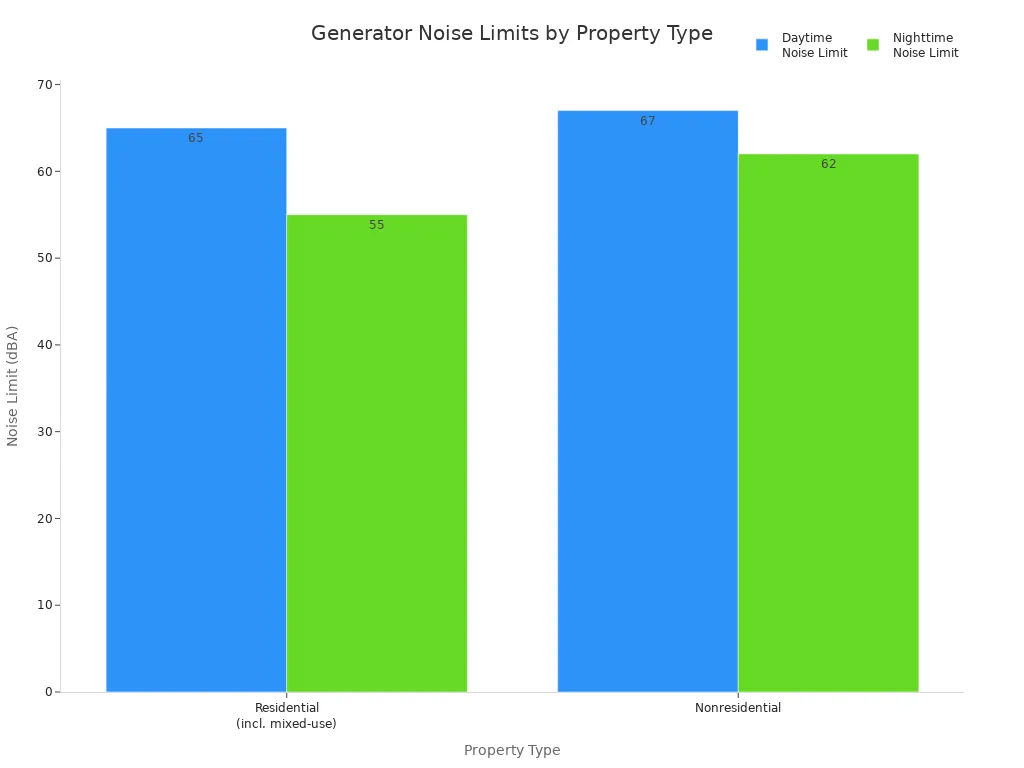
Noise level matters for comfort and rules. Most generators make 60-70 dB, like talking. Loud ones can reach 100 dB and hurt hearing. Local rules limit noise, especially at night.
Property Type | Daytime Noise Limit (dBA) | Nighttime Noise Limit (dBA) |
|---|---|---|
Residential (including mixed-use zones) | 65 | 55 |
Nonresidential | 67 | 62 |
Run time depends on tank size, load, and generator size. Longer run times need bigger tanks and better cooling. Check local rules for allowed run times.
The nameplate gives you key generator facts. You see power, voltage, phase, frequency, model, and serial number. It also shows safety marks and date made. Use this for setup, care, and warranty.
Fuel pressure and BTU ratings show fuel needs and heat.
Safety features protect you from danger. Look for built-in CO safety, transfer switches, strong cords, and backfeed protection.
Safety Feature | Description and Protective Function |
|---|---|
Built-in CO Safety Technology | Finds bad carbon monoxide and shuts off the generator. |
Transfer Switch Installation | Connects generator to panel safely, stopping electrical danger. |
Heavy-Duty Extension Cords | Rated for load, three prongs, protects against shock outside. |
Avoid Backfeeding | Stops powering home wires by outlet, lowers shock and fire risk. |
You need regular care to keep your generator working.
Maintenance Interval | Typical Tasks |
|---|---|
Weekly | Start and run generator, check for leaks, check alarms, check fuel, check breaker. |
Monthly | Clean area, check oil and coolant, check battery, check wires, drain water. |
Semi-Annual | Battery check, look at belts, heater, exhaust, air filters, hoses, grease. |
Annual | Check alternator, transfer switch, change filters, spark plugs, clean crankcase, flush coolant, load test. |
If you want strong, clean power, look at LIYU Group's gas generators and container sets. These generators give lots of power, low pollution, and easy setup. Container sets make setup fast and simple. You get strong work, easy care, and help for many uses. LIYU Group's products fit homes, shops, and factories. You can trust their specs for safety and good work.
Recommendation: Try LIYU Group's gas generators for strong power and easy setup.
When you check generator spec sheets, you will see ratings tables. These tables show the main numbers for each generator. You can find power output, voltage, current, and frequency. Each row shows a different setting or condition. You can look at models side by side. This helps you choose the best generator for your needs.
Power output tells how much electricity the generator gives.
Voltage and current help you see if it fits your equipment.
Frequency (usually 60 Hz) shows if it matches your local grid.
Tip: Always look at the ratings table on generator spec sheets. It helps you avoid mistakes and makes picking easier.
Certifications on generator spec sheets show if the generator meets safety and quality rules. You will often see marks like ANSI, UL, CSA, and NSF. These marks mean the maker tested the generator and it passed tough rules.
ANSI: American National Standards Institute
UL: Underwriters Laboratories
CSA: Canadian Standards Association
NSF: National Sanitation Foundation
You might also see EPA Tier ratings. These ratings show the generator meets Environmental Protection Agency rules for emissions. It means the generator makes less pollution and follows the law.
Note: Certifications keep you and your equipment safe. Always check for them on generator spec sheets.
The starting system and control panel make the generator easy to use. Many generators have automatic starting systems. When the power goes out, the generator starts by itself. It uses a transfer switch to sense when power drops and turns on. When power comes back, it shuts off safely.
Control panels let you see and manage the generator. You can check voltage, current, and frequency on the display. Modern panels use microprocessors and sensors. They watch for problems like overheating and low oil. If something is wrong, the panel can shut down the generator to stop damage.
Feature | Residential Generator Control Panels | Industrial Generator Control Panels |
|---|---|---|
Size and Placement | Small, on the generator | Large, separate units |
Complexity | Simple, basic monitoring | Advanced, load management |
User Interface | Easy to use | Robust, automated |
Automation | Basic, often with transfer switch | Full automation, multi-unit control |
Customization | Limited | High, many options |
You can watch the generator close by or from far away. Some panels send alerts or let you control the generator from another place. This makes using the generator safe and simple.
When you compare generator spec sheets, you want to see differences quickly. You can use charts or tables to line up each generator's power output, voltage, and other key features. This makes it easy to spot which generator fits your needs best.
Create a simple table. List each generator model across the top. Put important features like power output, voltage, fuel type, and run time down the side.
Use color or icons to highlight the best values. Green can show the top choice for power or output. Red can mark options that do not meet your needs.
Try comparison infographics. These show features in the middle and use images to help you recognize each generator.
Make pros and cons lists for each generator. Place them side by side. Use bold headers and icons to make the lists easy to scan.
Use Excel or online tools to build charts. These can show power output, noise level, and cost in a visual way.
Tip: Keep your comparison simple and visual. This helps you process information faster and make a smart choice.
Many people make mistakes when comparing generator spec sheets. You can avoid these by watching for a few key problems:
Skipping research on the right size. If you pick a generator that is too small, it will not give enough power. If it is too large, you waste money and fuel.
Looking only at price. Cheap generators often have lower quality. They may cost more over time because of repairs or poor power output.
Buying from dealers who lack experience. This can lead to trouble with support, warranty, or getting the right parts.
Note: Always check the dealer's reputation and look for expert advice. Most buyers talk to experts or electricians before choosing a generator. They help you match the generator's power output and specifications to your needs. This step keeps your project safe and saves money in the long run.
You can read a generator spec sheet by doing these things:
Think of the generator spec sheet like a plan.
Look at how much power it gives and what kind of battery it needs. Check what fuel it uses.
Make sure the voltage and phase match your system.
Look at how the generator cools itself. Check the transfer switch and engine parts.
Talk to experts if you have questions about setting up or taking care of the generator.
Make sure the generator's power fits your needs and the place you want to put it.
Knowing generator specs helps you pick the right one. You choose the best power, phase, and fuel for your job. You lower problems when you set up the generator and keep things safe.
If you want strong and clean power, look at LIYU Group's gas generators or their container sets. Contact them to learn more or get help with your next generator setup.
The power rating tells how much electricity the generator makes. You use this number to see if the generator is strong enough. Always check if it gives enough power for your things.
You should check your generator once a week. Run it, look for leaks, and check the fuel. Every month, clean around it and check the oil. Yearly checks help keep it safe and working right.
No, you cannot use just any fuel. Each generator needs a certain fuel. Some use diesel, others use natural gas or propane. Always read the spec sheet before putting in fuel.
Generator noise level can bother people and break rules. Loud generators can make neighbors upset. Pick a generator that is quiet enough for your area.
First, write down what you want to power. Add up the total wattage. Make sure the voltage and phase match your system. Look at the fuel type and the size. Use a table to compare each generator.
Step | What to Do |
|---|---|
List equipment | Write down all devices |
Check wattage | Add up total power needed |
Match voltage/phase | See if it fits your system |
Pick fuel type | Choose what you can supply |
Compare generators | Use a chart or table |
Tip: Ask an expert if you are not sure which generator to get.
Liyu Group Participates in Madagascar Government Delegation Forum
Liyu Group Invited to the China-Zambia Green Power Cooperation Forum
What Types of Facilities Benefit From Used Commercial Generators?
How Fuel Polishing Improves The Efficiency of Diesel Generators?
How Tariffs Could Potentially Impact The Generator Industry?