Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-10 Origin: Site
Hertz tells you how many times the current switches direction in your generator. You must know the correct frequency to keep your power safe and steady. If you set the generator frequency wrong, your electricity may not work right. Your generator should match what your devices need.
You keep your equipment safe when you check the hertz and frequency.
You make sure your power works well when you watch the generator frequency.
Hertz (Hz) tells how often the electric current switches direction each second in your generator.
Setting your generator to the right frequency (50 Hz or 60 Hz) keeps your devices safe and helps them work well.
Use tools like digital multimeters to check and change your generator's frequency correctly.
The wrong frequency can hurt motors, transformers, and sensitive electronics, which can lead to expensive repairs.
Check and take care of your generator often to keep the frequency steady and protect your power supply.
When you check your generator's details, you see hertz listed. Hertz (Hz) tells you how often the current changes direction each second. For generators, frequency means how many AC cycles happen every second. The generator spins magnetic poles inside the alternator. One full spin makes one AC cycle. If your generator makes 60 cycles in one second, it runs at 60 Hz. You must set the generator frequency to match your area's standard. This keeps your power steady and protects your equipment.
Tip: Always look at the hertz rating before you plug in any device. Doing this helps you stop damage and keeps your electricity working well.
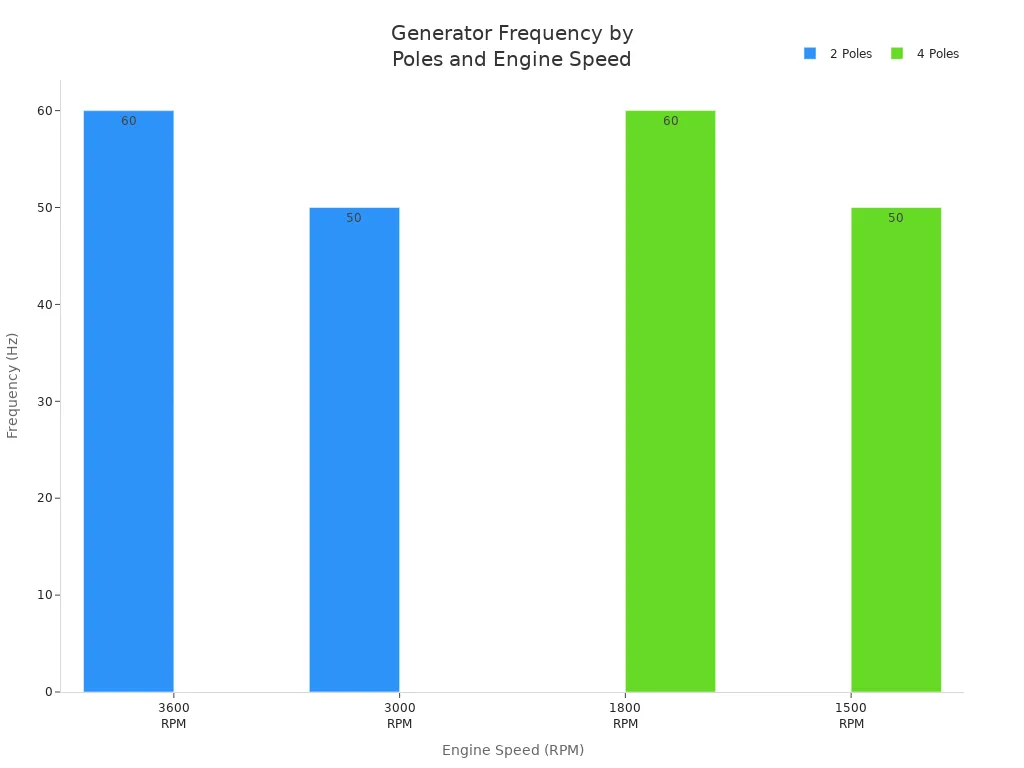
Generator frequency depends on engine speed and the number of magnetic poles. There is a simple formula you can use:
Frequency (Hz) = (Engine Speed in RPM x Number of Poles) / 120
Here are some examples:
Generator Poles | Frequency (Hz) | Engine Speed (RPM) |
|---|---|---|
2 | 60 | 3600 |
2 | 50 | 3000 |
4 | 60 | 1800 |
4 | 50 | 1500 |
Changing engine speed or pole count changes the frequency. If you want 60 cycles per second, set the engine speed and pole number right. A 2-pole generator at 3600 RPM gives 60 Hz. A 4-pole generator at 1800 RPM also gives 60 Hz. This formula helps you set your generator for the correct output.
You might ask why 50 Hz and 60 Hz are used most around the world. The reason comes from history and engineering. In North America, engineers picked 60 Hz because it worked well for generator design and transformers. It let motors run faster and made them smaller. In Europe, companies chose 50 Hz to fit their metric system and help power travel far. These choices became the standard as more countries built their power systems.
Historical Basis: Early power systems used many frequencies. The US chose 60 Hz in 1891.
Technical Considerations: 60 Hz gave better motor performance. It made generators smaller and lighter.
Economic Factors: Using one frequency made it easier to build big power networks.
European Choice: The UK and EU picked 50 Hz so countries could work together.
You need to know which standard your area uses. Most of North America and some parts of Asia use 60 Hz. Europe, Africa, and Australia use 50 Hz. Setting your generator frequency keeps your voltage and power safe and steady.
You must match generator frequency to your devices. Most equipment works best at a certain hertz, like 50 Hz or 60 Hz. If you use the wrong frequency, your devices may not work right. Motors might spin too fast or too slow. Transformers can get too hot. Some electronics, like microwaves or medical machines, may stop working if the frequency changes even a little.
Note: Devices such as elevators, programmable logic controllers, and fire pump motors need steady voltage and frequency. Even small changes in frequency can make them stop or break.
Generator frequency changes how fast AC motors run and how transformers work. Using the wrong frequency can make a device wear out faster or break. For example, a refrigerator made for 50 Hz may not work well on 60 Hz. This can be unsafe and make your equipment last less time. Sensitive electronics, like computers and UPS systems, need steady power. Changes in frequency can set off alarms or shut things down.
Where you live matters too. Europe, Asia, and Africa use 50 Hz. North America uses 60 Hz. Japan uses both. Always check your generator's frequency before you plug in devices.
Aspect | 50 Hz Systems | 60 Hz Systems |
|---|---|---|
Regional Usage | Europe, Asia, Africa | North America, Caribbean |
Motor Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
Transformer Design | Larger | Smaller |
Generator Size and Weight | Larger | More compact |
Equipment Output | Lower | Higher |
You keep your power steady when you control generator frequency. If the frequency changes too much, big problems can happen. Wrong frequency can blow fuses or trip relays. It can even hurt the generator shaft. Sudden changes in voltage and frequency can make your power grid unstable. This can cause blackouts or damage your equipment.
Tip: Always watch voltage and frequency. Steady output means safer electricity for your home or business.
Keeping frequency steady helps balance electricity supply and demand. If your generator cannot keep up with changes, frequency drops. This can make sensitive equipment stop working. Good control and tight rules help stop these problems. When you use more than one generator, matching frequency keeps power steady. It also helps stop overloads and keeps your power grid safe.
Frequency changes can also hurt the whole power grid. Bad control or broken wires can make it hard to keep frequency steady. Regular checks and good care keep your generator working well and protect your devices from harm.
You need special tools to check generator frequency. Using these tools helps you get the right results. The most common tool is a digital multimeter with a frequency function. It shows the number clearly, so you do not have to guess. You can also use power quality analyzers, power analyzers, or oscilloscopes. Each tool works in its own way.
Here is a table to help you pick the best tool for measuring generator frequency:
Instrument Type | Description | Suitability for Field Frequency Measurement |
|---|---|---|
Digital Multimeters | Show frequency as a number, so you make fewer mistakes; they also measure voltage and current | Very good for field use because they are easy to carry and use |
Power Quality Analyzers | Measure frequency, voltage, current, power, and waveforms to find power problems | Good for detailed power system checks |
Power Analyzers | Measure voltage, current, and power very accurately, including main and extra frequencies | Good for exact frequency checks, including extra frequencies |
Oscilloscopes | Let you see frequency waveforms and measure voltage | Good for looking at waveforms but not as easy for simple frequency checks |
Tip: Digital multimeters with a frequency function are the easiest and most accurate for field work. They are simple to carry and safe to use.
When you measure generator frequency, follow these steps for the best results:
Use standard tools for measuring generator frequency, like a digital multimeter, frequency counter, or oscilloscope.
Make sure your tool is calibrated. This keeps your measurement correct.
Set the tool's frequency range and input sensitivity to match what you expect.
Connect the probes tightly so your readings do not jump around.
For oscilloscopes, set the time base and voltage scale to see the waveform well.
Check your frequency reading with a known reference if you can.
Keep records of calibration for your frequency monitoring tools.
Note: Always measure generator frequency in a safe, dry place. Do not touch live wires. Wear safety gear when you do maintenance.
You must set your generator frequency to match your area's hertz standard. Most places use 50 Hz or 60 Hz. The output frequency depends on engine speed and magnetic poles. If you want to change the frequency, you need to change the engine speed.
Follow these steps to set the right generator frequency:
Read your operator's manual. Stop the engine and let it cool before you start.
Remember, frequency output depends on engine speed. For 60 Hz, set a 2-pole generator to 3600 RPM.
Find the governor throttle adjustment screw. It usually has yellow paint and a spring.
Use a digital multimeter with a frequency function or a Hz meter to check the output.
Turn the governor screw clockwise to make speed and frequency go up. Turn it the other way to make them go down. Try to get a frequency between 60-62 Hz.
Plug in a normal load while you adjust. This helps you see if the generator frequency stays steady when used.
Never adjust by ear. Do not go past the recommended RPM. Too much speed can hurt the engine and lower voltage.
After you set the frequency, check the voltage. Change it if you need to.
Alert: If you cannot keep the frequency steady, or if the frequency stays too high or low, call a professional. Wrong adjustment can hurt your generator and devices.
Changing generator speed changes the output frequency. When you add more load, speed and frequency can drop. The governor senses this and adds fuel to bring them back up. If you lower engine speed, frequency and voltage go down. If you raise speed, both go up. Keeping the right frequency is part of good maintenance.
Steady generator frequency keeps your power safe. If you do not keep it steady, you can get big current surges, blown fuses, and broken equipment. Turbine blades and motors can break if frequency goes outside safe limits. Many devices, like clocks and motors, need steady frequency to work right. Unsteady frequency can cause trips that shut down your power.
Maintenance Reminder: Check generator frequency and voltage often. Use frequency monitoring tools to find problems early. Good care and regular checks protect your generator and your electricity.
If you use the wrong frequency, your equipment can have big problems. Your devices are not safe if the generator frequency is wrong. Big machines and three-phase equipment are in the most danger. They do not work right if the frequency does not fit their design. This can cause damage or make them wear out faster. If you plug in equipment made for 50 Hz to a 60 Hz source, it can get too hot or break quickly. Small electronics, like phone chargers and laptops, usually work with both 50 Hz and 60 Hz. They have special power supplies that change to fit different frequencies.
Here are some types of equipment that are most at risk:
Large motors and pumps
Three-phase industrial machines
HVAC systems
Elevators and lifts
Medical devices made for one frequency
Alert: Always look at the frequency rating before you plug in any device to your generator. This helps protect your devices and keeps your electricity safe.
You might see signs of damage if there are frequency problems. Watch for these warning signs:
Things get hot or smell like burning
Strange noises, shaking, or buzzing
Motors do not start or stop working often
Screens flicker or go blank
Power shuts off suddenly or goes away
If you spot these problems early, you can stop bigger failures and save money on repairs.
If you notice frequency problems, you should act quickly. First, check if your generator has too many things plugged in. Unplug things you do not need and see if the frequency gets better. Make sure you have enough fuel and clean air filters. Look at the governor and springs to see if they control speed right. Check spark plugs and oil levels to help the engine run well. Look at any error codes on your generator's screen.
Try these steps to fix frequency problems:
Take off extra loads to help frequency stay steady.
Check fuel and air supply.
Look at governor parts and springs.
Change old spark plugs.
Make sure oil levels are good.
Read error codes for more help.
Restart the generator after unplugging everything.
Frequency problems often happen when the power your generator makes does not match what you plug in. Fast changes in load or engine speed can make the frequency go up or down. By watching these changes, you can find the problem and fix it before your equipment gets hurt.
Tip: Doing regular checks and fixing problems fast keeps your generator frequency steady and your power working well.
You help your generator stay safe by checking frequency often. Doing regular checks lets you find problems early and keep your equipment safe.
You can make your generator frequency more steady by doing these things:
Turn on your generator every month with things plugged in.
Watch the voltage and frequency when you test it.
Look at the oil, coolant, and battery before each use.
Change filters and spark plugs when they get old.
Have a professional check your generator once a year.
If you have hard problems or repairs, call a certified expert. Always use your owner's manual for tips on taking care of your generator.
Your devices may not work right. Motors can get hot or break. Screens may flicker. You risk damaging your equipment. Always check the hertz before you use your generator.
You can use frequency monitoring equipment like a digital multimeter. Connect it to the generator output. Read the number on the screen. It shows the frequency in hertz.
You can adjust the engine speed using the governor screw. Turn it slowly and watch the frequency. Use a meter to check your results. If you cannot set it right, call a professional.
Countries picked their standards long ago. North America uses 60 Hz. Europe, Asia, and Africa use 50 Hz. You must match your generator to your local standard.
Load frequency control helps keep the generator frequency steady when you add or remove devices. It stops big changes in power. This keeps your equipment safe.
Tip: Always test your generator under normal load to see if the frequency stays steady.