Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-25 Origin: Site
You find 4-stroke engines in many generators because they provide steady power and are compact. These engines operate through four steps: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. Each step ensures the engine runs efficiently and quietly. With 4-stroke engines, you get easy starting, quiet operation, and the flexibility to use different fuels.
You receive steady AC power.
Maintenance is simple and straightforward.
They are versatile for use in various situations, including emergencies.
A 4-stroke engine has four steps. These are intake, compression, power, and exhaust. These steps help turn fuel into steady power.
These engines last longer than 2-stroke engines. They use fuel better and make less pollution. This makes them good for generators.
You should check the oil, spark plug, and valves often. This helps your 4-stroke engine run well and last longer.
You see 4-stroke engines in many machines like generators. A four-stroke engine is a kind of internal combustion engine. The piston moves four times to finish one cycle. This design makes the engine strong and good at making power.
Imagine a four-stroke engine as a machine that changes fuel into energy. It does this by following a few steps. Each step helps the engine run well and give steady power.
Here is how a four-stroke engine works by mechanical engineering rules:
Intake Stroke: The piston goes down. The intake valve opens. Air and fuel go inside the cylinder.
Compression Stroke: The piston goes up. It squeezes the air-fuel mix. Pressure and heat get higher.
Power Stroke: The spark plug lights the mix. The explosion pushes the piston down. The engine makes work.
Exhaust Stroke: The piston goes up again. Burned gases leave through the exhaust valve.
This cycle needs two turns of the crankshaft. You find these four strokes in every 4-stroke engine. Each stroke does a special job. This keeps the engine running well and makes it quieter.
Stroke | Piston Movement | Valve Action | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
Intake | Down | Intake opens | Air-fuel enters |
Compression | Up | Both closed | Mixture compressed |
Power | Down | Both closed | Energy produced |
Exhaust | Up | Exhaust opens | Gases expelled |
You get many good things from 4-stroke engines. They last a long time and do not need much fixing. This engine design gives you steady power for your generator.
A four-stroke engine works in four main steps. Each step helps turn fuel into power. The engine repeats these steps to keep your generator working well.
Intake Stroke: The piston goes down inside the cylinder. The intake valve opens up. Air and fuel go into the cylinder. The air goes through a filter. The fuel mixes in or gets injected.
Compression Stroke: The piston moves up. Both valves stay closed. The piston squeezes the air and fuel together. This makes the pressure and temperature rise.
Power Stroke: The spark plug fires before the piston reaches the top. The air and fuel explode. This pushes the piston down. That movement makes power for the crankshaft.
Exhaust Stroke: The exhaust valve opens. The piston moves up again. It pushes out the burned gases. This clears the cylinder for the next cycle.
The strokes always happen in the same order. The engine needs two crankshaft turns for one full cycle. This timing helps the engine run smooth and well.
Here is a table that shows how the piston moves in each stroke:
Stroke | Piston Movement Direction | What Happens in the Cylinder |
|---|---|---|
Intake Stroke | Down (TDC to BDC) | Air and fuel enter as the intake valve opens |
Compression Stroke | Up (BDC to TDC) | Piston squeezes the air and fuel, both valves closed |
Power Stroke | Down (TDC to BDC) | Explosion pushes the piston down, making work |
Exhaust Stroke | Up (BDC to TDC) | Piston pushes out gases through the open exhaust valve |
Each stroke has its own job. The intake stroke brings in air and fuel. The compression stroke squeezes them tight. The power stroke makes energy. The exhaust stroke removes waste. The cycle keeps going while the engine runs.
A generator uses a four-stroke engine that follows this cycle. The engine needs two crankshaft turns for every full cycle. Each stroke is half a turn of the crankshaft. If the cylinder fires 200 times in a minute, the crankshaft turns 400 times. This 2:1 ratio keeps the engine steady and balanced.
The piston moves up and down in the cylinder. In the intake stroke, it goes down to let air and fuel in. The compression stroke pushes the piston up to squeeze the mix. The power stroke sends the piston down, turning fuel into motion. The exhaust stroke moves the piston up to push out gases.
The four-stroke cycle helps the generator engine work well. The design keeps heat low and moves energy to the crankshaft better. The engine's shape, like the stroke-to-bore ratio, changes how it uses fuel and handles heat. When the engine works hard, it wastes less energy. When it works less, it may lose some efficiency because of pumping losses and not burning all the fuel.
A four-stroke engine gives steady power and uses fuel better in your generator. The cycle keeps the engine cool, lowers wear, and cuts down on emissions. This makes 4-stroke engines a good choice for reliable power.
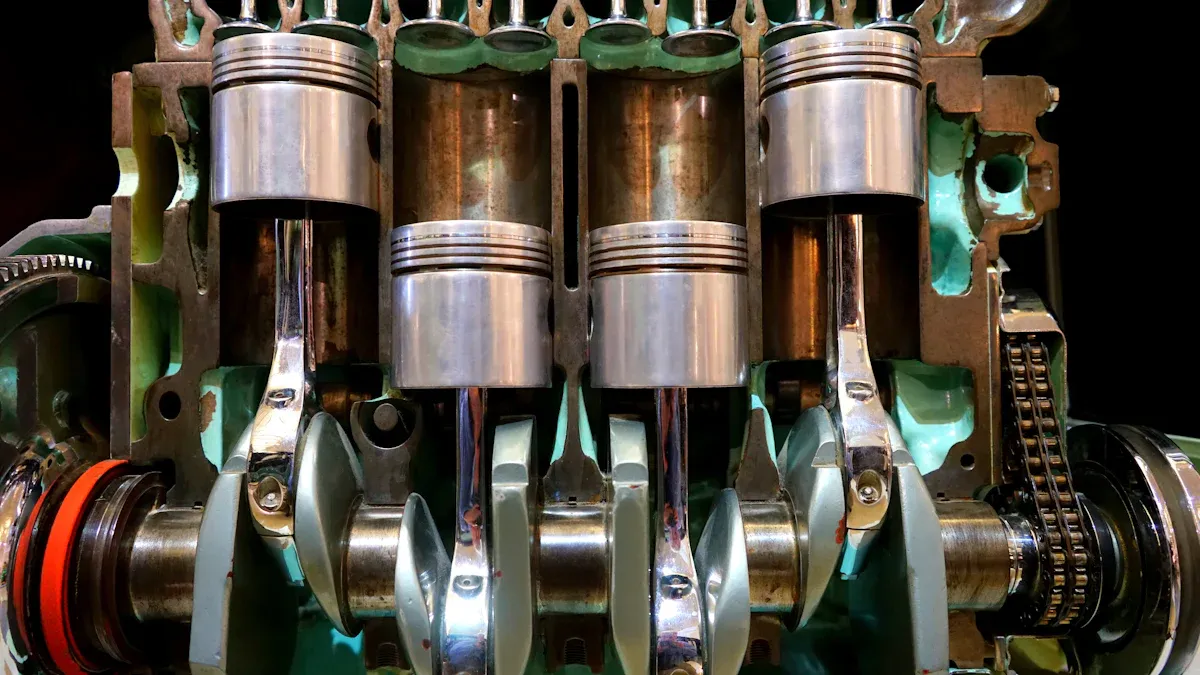
A 4-stroke engine uses several main parts to turn fuel into power for your generator. Each part has a special job. When you know how these parts work together, you can better care for your generator.
The piston moves up and down inside the cylinder. It creates the motion needed for each stroke. The cylinder holds the piston and forms the space where fuel burns. You see this process in every 4-stroke engine:
The piston moves down. The intake valve opens. Air and fuel enter the cylinder.
The piston moves up. Both intake and exhaust valves close. The mixture gets squeezed.
The spark plug fires. The piston moves down. Power goes to the crankshaft.
The piston moves up. The exhaust valve opens. Gases leave the cylinder.
Piston rings seal the space between the piston and cylinder. This keeps the combustion chamber airtight and efficient.
The crankshaft changes the piston's up-and-down motion into spinning motion. The camshaft controls the timing of the intake and exhaust valves. It turns at half the speed of the crankshaft. This timing lets the valves open and close at the right moments. When the crankshaft moves, it drives the camshaft. The camshaft then moves the intake and exhaust valves so the engine runs smoothly.
The intake and exhaust valves open and close to let air and fuel in and push gases out. The spark plug lights the fuel-air mix at just the right time. Here is how they work in each stroke:
Intake valve opens. Air and fuel enter.
Both valves close. The piston compresses the mix.
Spark plug fires. Both valves stay closed. The piston moves down.
Exhaust valve opens. Gases leave the cylinder.
The intake and exhaust valves must work in perfect order. If they do not, the engine loses power or stops.
Tip: Regularly check the spark plug and valves. Clean or replace them to keep your 4-stroke engine running well.
A 4-stroke engine has a dedicated oil reservoir. The oil sump stores lubricant and helps cool the engine when it is off. The oil pump moves oil to all moving parts. Oil filters remove dirt, keeping the oil clean. The lubrication system reduces friction and wear on the crankshaft, pistons, and intake and exhaust valves. This keeps the engine reliable and extends its life.
Main Components Table
Component | Function |
|---|---|
Piston | Moves up and down, creates motion |
Cylinder | Houses piston, forms combustion chamber |
Crankshaft | Converts motion to spinning power |
Camshaft | Controls intake and exhaust valves |
Intake Valve | Lets air and fuel in |
Exhaust Valve | Pushes gases out |
Spark Plug | Ignites fuel-air mixture |
Oil Reservoir | Stores and cools engine oil |
Oil Pump/Filter | Circulates and cleans oil |
You find these parts in quality generators like those from LIYU Group. Their gas generator and containerized gas generator set use these 4-stroke engine components for steady, reliable power. If you want a generator that lasts, consider products from LIYU Group.
You might wonder which engine saves more fuel. A 4-stroke engine keeps intake and exhaust strokes apart. This helps it burn fuel better. Oil does not mix with gasoline in a 4-stroke engine. That means you use less fuel. In a 2-stroke engine, some fresh fuel escapes out the exhaust. This wastes fuel and makes more pollution. Oil mixes with fuel in a 2-stroke engine. This makes burning less complete.
Aspect | 2-Stroke Engines | 4-Stroke Engines |
|---|---|---|
Fuel Efficiency | Less efficient; oil mixed with fuel leads to higher consumption | More efficient; separate intake and exhaust strokes allow precise combustion |
Lubrication | Oil mixed with fuel, causing less efficient combustion | Dedicated lubrication system improves fuel economy |
Typical Generator Use | Small, portable emergency generators | Larger generators for construction sites, homes, businesses |
Advantages | Lightweight, compact | Fuel efficiency, durability, long-term reliability |
A 2-stroke engine makes more dirty exhaust. It lets out more unburned fuel and pollution. A 4-stroke engine keeps intake and exhaust apart. This makes cleaner air. It helps you follow environmental rules and keeps the air safer.
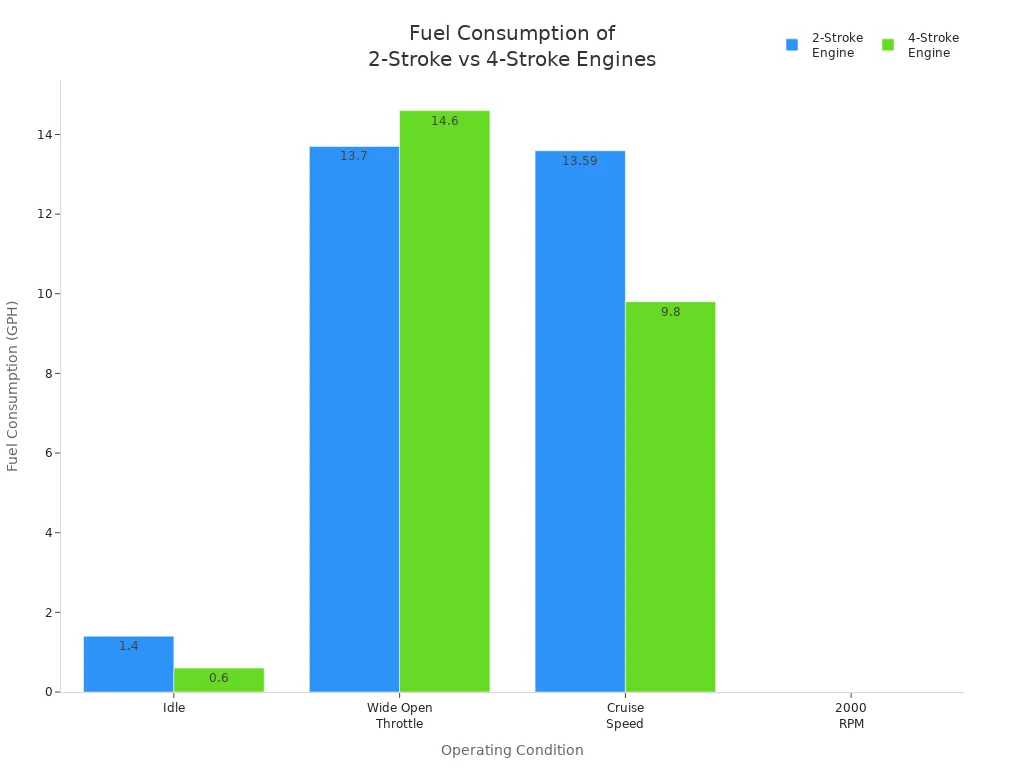
You want an engine that lasts longer and needs less fixing. A 4-stroke engine can go longer between services. You change its oil every 100 hours or once a year. The oil filter gets changed every 200 hours. You check and set the valve clearance every 300 hours. Each day, you check oil, look for leaks, and clean the air inlet. A 2-stroke engine is easier to fix but wears out faster. It needs repairs more often.
Engine Type | Maintenance Interval and Characteristics |
|---|---|
2-Stroke Engine | Easier and cheaper to maintain; shorter lifespan; more frequent repairs due to increased wear and tear |
4-Stroke Engine | More complex and costly maintenance; longer service intervals; tends to outlast 2-stroke engines due to reduced engine stress |
You find 4-stroke engines in bigger machines like lawn tractors and home generators. They give smoother power and save more fuel. 2-stroke engines are in small tools you hold in your hand. They work in any position and are lighter.
Tip: Pick a 4-stroke engine for your generator if you want to save fuel, have cleaner air, and make your engine last longer.
If you want to know more information about the difference between 2-stoke engine and 4-stoke engine, please read this article: 2-stoke vs. 4-stoke engine.
You have learned how 4-stroke engines help your generator work. These engines have tough parts and a clever design. They give steady power, make less pollution, and last a long time.
4-stroke engines move slower, so they do not wear out fast.
Their oil system is separate and protects the engine parts.
Knowing these basics helps you keep your generator in good shape.
LIYU Group sells gas generators and containerized sets you can trust. Check out their products if you want power you can count on.
You should change the oil every 100 hours of use or once a year. Clean oil helps your engine last longer and run smoothly.
Most 4-stroke generators use gasoline. Some models accept propane or natural gas. Always check your manual for the correct fuel type.
A 4-stroke engine has a separate oil system. It reduces wear and keeps parts cool. You get longer life and fewer repairs.
Engine Type | Lifespan |
|---|---|
2-Stroke | Shorter |
4-Stroke | Longer |
Liyu Group Participates in Madagascar Government Delegation Forum
Liyu Group Invited to the China-Zambia Green Power Cooperation Forum
What To Know before Installing A Backup Commercial Generator?
What Types of Facilities Benefit From Used Commercial Generators?
How Fuel Polishing Improves The Efficiency of Diesel Generators?
How Tariffs Could Potentially Impact The Generator Industry?